Mutant p53 drives clonal hematopoiesis through modulating epigenetic pathway
- PMID: 31827082
- PMCID: PMC6906427
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13542-2
Mutant p53 drives clonal hematopoiesis through modulating epigenetic pathway
Erratum in
-
Author Correction: Mutant p53 drives clonal hematopoiesis through modulating epigenetic pathway.Nat Commun. 2020 Jul 28;11(1):3856. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-17555-0. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32724180 Free PMC article.
Abstract
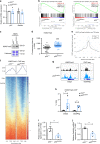
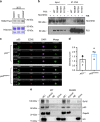
Clonal hematopoiesis of indeterminate potential (CHIP) increases with age and is associated with increased risks of hematological malignancies. While TP53 mutations have been identified in CHIP, the molecular mechanisms by which mutant p53 promotes hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell (HSPC) expansion are largely unknown. Here we discover that mutant p53 confers a competitive advantage to HSPCs following transplantation and promotes HSPC expansion after radiation-induced stress. Mechanistically, mutant p53 interacts with EZH2 and enhances its association with the chromatin, thereby increasing the levels of H3K27me3 in genes regulating HSPC self-renewal and differentiation. Furthermore, genetic and pharmacological inhibition of EZH2 decreases the repopulating potential of p53 mutant HSPCs. Thus, we uncover an epigenetic mechanism by which mutant p53 drives clonal hematopoiesis. Our work will likely establish epigenetic regulator EZH2 as a novel therapeutic target for preventing CHIP progression and treating hematological malignancies with TP53 mutations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- F32 CA203049/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA134777/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R35 GM133496/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL150624/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- K08 CA197369/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001108/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK105014/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 DK106846/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA101937/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL140961/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 DK119524/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL146137/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

