Structural Basis for Finding OG Lesions and Avoiding Undamaged G by the DNA Glycosylase MutY
- PMID: 31829624
- PMCID: PMC7069122
- DOI: 10.1021/acschembio.9b00639
Structural Basis for Finding OG Lesions and Avoiding Undamaged G by the DNA Glycosylase MutY
Abstract
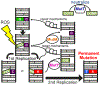
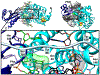
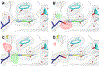
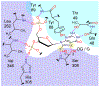
The adenine glycosylase MutY selectively initiates repair of OG:A lesions and, by comparison, avoids G:A mispairs. The ability to distinguish these closely related substrates relies on the C-terminal domain of MutY, which structurally resembles MutT. To understand the mechanism for substrate specificity, we crystallized MutY in complex with DNA containing G across from the high-affinity azaribose transition state analogue. Our structure shows that G is accommodated by the OG site and highlights the role of a serine residue in OG versus G discrimination. The functional significance of Ser308 and its neighboring residues was evaluated by mutational analysis, revealing the critical importance of a β loop in the C-terminal domain for mutation suppression in cells, and biochemical performance in vitro. This loop comprising residues Phe307, Ser308, and His309 (Geobacillus stearothermophilus sequence positions) is conserved in MutY but absent in MutT and other DNA repair enzymes and may therefore serve as a MutY-specific target exploitable by chemical biological probes.
Figures


References
-
- Lindahl T (1993) Instability and Decay of the Primary Structure of DNA. Nature 362, 709–715. - PubMed
-
- Steenken S, and Jovanovic SV (1997) How Easily Oxidizable Is DNA? One-Electron Reduction Potentials of Adenosine and Guanosine Radicals in Aqueous Solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc 119, 617–618.
-
- Ito R, Hayakawa H, Sekiguchi M, and Ishibashi T (2005) Multiple Enzyme Activities of Escherichia Coli MutT Protein for Sanitization of DNA and RNA Precursor Pools. Biochemistry 44, 6670–6674. - PubMed
-
- Maki H, and Sekiguchi M (1992) MutT Protein Specifically Hydrolyses a Potent Mutagenic Substrate for DNA Synthesis. Nature 355, 273–275. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

