Mammalian phospholipase D: Function, and therapeutics
- PMID: 31830503
- PMCID: PMC7233427
- DOI: 10.1016/j.plipres.2019.101018
Mammalian phospholipase D: Function, and therapeutics
Abstract
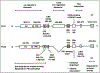
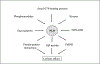
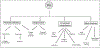
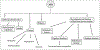
Despite being discovered over 60 years ago, the precise role of phospholipase D (PLD) is still being elucidated. PLD enzymes catalyze the hydrolysis of the phosphodiester bond of glycerophospholipids producing phosphatidic acid and the free headgroup. PLD family members are found in organisms ranging from viruses, and bacteria to plants, and mammals. They display a range of substrate specificities, are regulated by a diverse range of molecules, and have been implicated in a broad range of cellular processes including receptor signaling, cytoskeletal regulation and membrane trafficking. Recent technological advances including: the development of PLD knockout mice, isoform-specific antibodies, and specific inhibitors are finally permitting a thorough analysis of the in vivo role of mammalian PLDs. These studies are facilitating increased recognition of PLD's role in disease states including cancers and Alzheimer's disease, offering potential as a target for therapeutic intervention.
Keywords: Lipid signaling; Membrane transport; Phosphatidic acid; Phospholipase D.
Copyright © 2019. Published by Elsevier Ltd.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural Insights for Drugs Developed for Phospholipase D Enzymes.Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2018;15(2):81-93. doi: 10.2174/1570163814666170816112135. Curr Drug Discov Technol. 2018. PMID: 28814238 Review.
-
Phospholipase D.Biochem Cell Biol. 2004 Feb;82(1):225-53. doi: 10.1139/o03-079. Biochem Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15052340 Review.
-
Overexpression of phospholipase D suppresses taxotere-induced cell death in stomach cancer cells.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 May;1783(5):912-23. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.11.019. Epub 2007 Dec 15. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18190795
-
Phospholipase D: a lipid centric review.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005 Oct;62(19-20):2305-16. doi: 10.1007/s00018-005-5195-z. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2005. PMID: 16143829 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phospholipid signalling through phospholipase D and phosphatidic acid.IUBMB Life. 2006 Aug;58(8):457-61. doi: 10.1080/15216540600871142. IUBMB Life. 2006. PMID: 16916782 Review.
Cited by
-
Interface of Phospholipase Activity, Immune Cell Function, and Atherosclerosis.Biomolecules. 2020 Oct 15;10(10):1449. doi: 10.3390/biom10101449. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 33076403 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidic Acid in Plant Hormonal Signaling: From Target Proteins to Membrane Conformations.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 17;23(6):3227. doi: 10.3390/ijms23063227. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35328648 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Phosphatidic acid is an endogenous negative regulator of PIEZO2 channels and mechanical sensitivity.Nat Commun. 2024 Aug 15;15(1):7020. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51181-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39147733 Free PMC article.
-
Phospholipase D1 promotes cervical cancer progression by activating the RAS pathway.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Aug;26(15):4244-4253. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17439. Epub 2022 Jun 30. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35775110 Free PMC article.
-
Arabidopsis PLDζ1 and PLDζ2 localize to post-Golgi membrane compartments in a partially overlapping manner.Plant Mol Biol. 2022 Jan;108(1-2):31-49. doi: 10.1007/s11103-021-01205-0. Epub 2021 Oct 2. Plant Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 34601701
References
-
- Hanahan DJ, Chaikoff IL, A new phospholipide-splitting enzyme specific for the ester linkage between the nitrogenous base and the phosphoric acid grouping, J. Biol. Chem 169 (3) (1947) 699–705. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan DJ, Chaikoff IL, The phosphorus-containing lipides of the carrot, J. Biol. Chem 168 (1) (1947) 233–240. - PubMed
-
- Hanahan DJ, Chaikoff IL, On the nature of the phosphorus-containing lipides of cabbage leaves and their relation to a phospholipide-splitting enzyme contained in these leaves, J. Biol. Chem 172 (1) (1948) 191–198. - PubMed
-
- Dohke Y, Fujita-Yoshigaki J, Sugiya H, Furuyama S, Hara-Yokoyama M, Involvement of phospholipase D in the cAMP-regulated exocytosis of rat parotid acinar cells, Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun 299 (4) (2002) 663–668. - PubMed
-
- Roth MG, Molecular mechanisms of PLD function in membrane traffic, Traffic 9 (2008) 1233–1239. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- BBS/E/B/0000C227/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- BBS/E/B/0000M243/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
- R35 GM131804/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- BB/P013384/1/BB_/Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council/United Kingdom
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

