The pro-apoptotic effect of a Terpene-rich Annona cherimola leaf extract on leukemic cell lines
- PMID: 31830975
- PMCID: PMC6909458
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-019-2768-1
The pro-apoptotic effect of a Terpene-rich Annona cherimola leaf extract on leukemic cell lines
Abstract
Background: The edible fruit Annona cherimola has previously shown many nutritional and medicinal properties. The current study evaluates the anti-cancer and anti-proliferative properties of Annona cherimola ethanolic leaf extract (AELE) on Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML) cell lines cultured in vitro (Monomac-1 and KG-1).
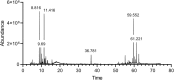
Methods: The anti-proliferative effect of A. cherimola ethanolic leaf extract was evaluated via cell viability assay. Its pro-apoptotic effect was assessed through Cell Death ELISA and dual Annexin V/PI staining. To further investigate the molecular mechanism by which the extract promoted apoptosis and inhibited the proliferation of the AML cells used, apoptotic protein expression was determined through western blots. Extract composition was elucidated by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS).
Results: Our results showed that the treatment with A. cherimola ethanolic leaf extract exhibited an inhibitory effect on the proliferation of both cancer cell lines used in a dose- and time-dependent manner, with no toxic effects on normal mononuclear cells (MNCs) isolated from human bone marrow. This effect was mediated by DNA fragmentation and apoptosis, as revealed by Cell Death ELISA and dual Annexin V/PI staining. Western blot analysis revealed a Bax/Bcl2 dependent mechanism of apoptosis, as well as PARP cleavage, confirming the apoptotic results observed previously. These effects may be attributed to the presence of terpenes which constitute a large component of the leafy extract, as revealed via GC-MS.
Conclusion: All the data presented in our study show that the terpene-rich A. cherimola ethanolic leaf extract exhibits an anti-proliferative and pro-apoptotic effect on the AML cell lines used.
Keywords: Acute myeloid leukemia; Annona cherimola; Apoptosis; Cancer; Terpenes.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures





References
-
- Dar RA, Shahnawaz M, Qazi PH. General overview of medicinal plants: A review. J Pharmacol. 2017;6(6):349–351.
-
- Roy A, Ahuja S, Bharadvaja N. A Review on Medicinal Plants against Cancer. 2017. p. 5.
-
- Ekor M. The growing use of herbal medicines: issues relating to adverse reactions and challenges in monitoring safety. Front Pharmacol. 2014; 10 [cited 2019 Mar 10];4. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3887317/. - PMC - PubMed
-
- WHO Guidelines on Safety Monitoring of Herbal Medicines in Pharmacovigilance Systems [Internet]. [cited 2019 Mar 10]. Available from: http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/en/m/abstract/Js7148e/
-
- Jantan I, Ahmad W, Bukhari SNA. Plant-derived immunomodulators: an insight on their preclinical evaluation and clinical trials. Front Plant Sci [Internet]. 2015 Aug 25 [cited 2019 Mar 10];6. Available from: https://www.frontiersin.org/article/10.3389/fpls.2015.00655/full - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

