Expanding the clinical and genetic spectrum of Heimler syndrome
- PMID: 31831025
- PMCID: PMC6909578
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-019-1243-x
Expanding the clinical and genetic spectrum of Heimler syndrome
Abstract
Background: Heimler syndrome (HS) is a rare hereditary systemic disorder, partial clinically overlapping with Usher syndrome. So far, our knowledge of HS is very limited, many cases are misdiagnosed or may not even be diagnosed at all. This study aimed to analyze the clinical and genetic characteristics of HS, and to evaluate potential phenotype-genotype correlations.
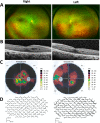
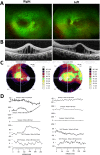
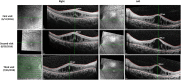
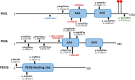
Results: Two HS cases caused by PEX1 mutations were identified, and a novel likely pathogenic mutation, PEX1 c.895_896insTATA, was found. The main ophthalmic finding of the two patients was consistent with retinitis pigmentosa accompanied by cystoid macular edema, but short axial length and hyperopia were also observed as two previously unreported ocular phenotypes. Analysis of the literature showed that of the 29 HS patients previously reported, 12 had PEX6 mutations, 10 had PEX1 mutations, two had PEX26 mutations, and the remaining patients were not genetically tested. Three novel genotype-phenotype correlations were revealed from analysis of these patients. First, most genotypes of every HS patient include at least one missense variant; second, at least one mutation in PEX1 or PEX6 gene affects the AAA-ATPase region in every HS patient with retinal dystrophy, suggesting AAA-ATPase region is a hypermutable region in patients with a retinal dystrophy; third, there are no significant differences between PEX1-, PEX6-, and PEX26-associated phenotypes.
Conclusion: Next-generation sequencing is important for the diagnosis of HS. This study expands the clinical and genetic spectrum of HS, and provides additional insights into genotype-phenotype correlations, which is vital for accurate clinical practice, genetic counseling, and pathogenesis studies.
Keywords: Genetic diagnosis; Genotype–phenotype; Heimler syndrome; Next-generation sequencing; PEX1; PEX6.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Spectrum of PEX1 and PEX6 variants in Heimler syndrome.Eur J Hum Genet. 2016 Nov;24(11):1565-1571. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2016.62. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Eur J Hum Genet. 2016. PMID: 27302843 Free PMC article.
-
Two siblings with Heimler syndrome caused by PEX1 variants: follow-up of ophthalmologic findings.Ophthalmic Genet. 2021 Aug;42(4):480-485. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2021.1923033. Epub 2021 May 6. Ophthalmic Genet. 2021. PMID: 33955814
-
Severe early onset retinitis pigmentosa in a Moroccan patient with Heimler syndrome due to novel homozygous mutation of PEX1 gene.Eur J Med Genet. 2016 Oct;59(10):507-11. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2016.09.004. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Eur J Med Genet. 2016. PMID: 27633571
-
Heimler Syndrome.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1299:81-87. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-60204-8_7. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 33417209 Review.
-
Ophthalmic Manifestations of Heimler Syndrome in Two Siblings With PEX1 Variants.J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2024 Jan-Feb;61(1):59-66. doi: 10.3928/01913913-20230220-01. Epub 2023 Apr 24. J Pediatr Ophthalmol Strabismus. 2024. PMID: 37092661 Review.
Cited by
-
Estimation of PEX1-mediated Zellweger spectrum disorder births and population prevalence by population genetics modeling.Genet Med Open. 2025 Apr 23;3:103431. doi: 10.1016/j.gimo.2025.103431. eCollection 2025. Genet Med Open. 2025. PMID: 40519747 Free PMC article.
-
PEX26 Functions as a Metastasis Suppressor in Colorectal Cancer.Dig Dis Sci. 2024 Jan;69(1):112-122. doi: 10.1007/s10620-023-08168-w. Epub 2023 Nov 13. Dig Dis Sci. 2024. PMID: 37957408
-
Identification of a Homozygous PEX26 Mutation in a Heimler Syndrome Patient.Genes (Basel). 2021 Apr 26;12(5):646. doi: 10.3390/genes12050646. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33926089 Free PMC article.
-
Management of oral manifestations of a child with Heimler Syndrome-2.BMJ Case Rep. 2024 Apr 24;17(4):e257354. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2023-257354. BMJ Case Rep. 2024. PMID: 38663901
-
Hereditary Hearing Impairment with Cutaneous Abnormalities.Genes (Basel). 2020 Dec 30;12(1):43. doi: 10.3390/genes12010043. Genes (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33396879 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ratbi I, Jaouad IC, Elorch H, Al-Sheqaih N, Elalloussi M, Lyahyai J, Berraho A, Newman WG, Sefiani A. Severe early onset retinitis pigmentosa in a Moroccan patient with Heimler syndrome due to novel homozygous mutation of PEX1 gene. Eur J Med Genet. 2016;59(10):507–511. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmg.2016.09.004. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Neuhaus C, Eisenberger T, Decker C, Nagl S, Blank C, Pfister M, Kennerknecht I, Muller-Hofstede C, Charbel Issa P, Heller R, et al. Next-generation sequencing reveals the mutational landscape of clinically diagnosed usher syndrome: copy number variations, phenocopies, a predominant target for translational read-through, and PEX26 mutated in Heimler syndrome. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2017;5(5):531–552. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.312. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

