FKB327, an adalimumab biosimilar, versus the reference product: results of a randomized, Phase III, double-blind study, and its open-label extension
- PMID: 31831079
- PMCID: PMC6909638
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-019-2046-0
FKB327, an adalimumab biosimilar, versus the reference product: results of a randomized, Phase III, double-blind study, and its open-label extension
Abstract
Objective: To compare the efficacy, serum drug concentrations, immunogenicity, and safety of FKB327 with the adalimumab reference product (RP) in combination with methotrexate in patients with moderate-to-severe, active rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
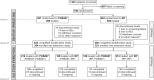
Methods: Patients were randomized 1:1 in a double-blind study (NCT02260791), received 40 mg of FKB327 or RP by subcutaneous injection every other week for 24 weeks (Period I), then re-randomized 2:1, remaining on the same study drug or switching to the other up to week 54 in an open-label extension (Period II, NCT02405780). Efficacy was evaluated using American College of Rheumatology (ACR20) response rate difference at week 24 with equivalence margins of ± 13% and - 12% to + 15% using 95% and 90% confidence intervals (CIs), respectively. Efficacy, serum drug concentrations, immunogenicity, and safety were compared at week 54.
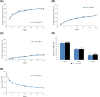
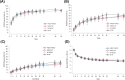
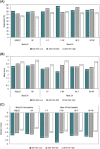
Results: A total of 730 patients were randomized in Period I (n = 367 FKB327, n = 363 RP), and 645 transitioned to Period II (n = 216 FKB327-FKB327, n = 108 FKB327-RP, n = 108 RP-FKB327, n = 213 RP-RP). At week 24, ACR20 response rates were 74.1% with FKB327 versus 75.7% with RP. 95% and 90% CI of the response rate difference were - 7.9 to 4.7% and - 7.3 to 3.6%, respectively, meeting predefined equivalence margins. The ACR20 response rate remained over 70% of patients to week 54 with all treatment sequences. In Period I, mean trough serum drug concentrations were slightly higher for patients receiving FKB327 than those receiving RP. Mean concentrations were stable over time and reflected steady state in Period II. The proportions of patients with samples positive for neutralizing antidrug antibodies (ADAs) were comparable (57.7% with FKB327 vs. 55.5% with RP) at week 24, and no consistent difference in ADA were seen between continuous and switched treatments in Period II. Efficacy was slightly reduced in the small proportion of patients with high ADA titers in all treatment groups. No clinically significant differences were observed in the incidence of commonly reported treatment-emergent adverse events between the treatments across Periods I and II.
Conclusion: FKB327 was equivalent to RP in clinical efficacy and demonstrated comparable safety and immunogenicity in patients with moderate-to-severe RA. No effect of switching between FKB327 and RP was observed.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02260791, Registered 29 July 2014. ClinicalTrials.gov, NCT02405780, Registered 17 July 2015.
Keywords: Adalimumab; Biosimilar; Comparative clinical trials; Efficacy; FKB327; Immunogenicity; Pharmacokinetics; Rheumatoid arthritis; Safety.
Conflict of interest statement
MCG has received grants from AbbVie, Amgen, and Pfizer. MCG has also received consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Galapagos, FKB, Gilead, UCB, Merck, Samsung, Novartis, Regeneron, and Sanofi. JG has received personal fees from FKB. MG reports grants from Fujifilm, AbbVie, Amgen, Gilead, Lilly, Merck, and Pfizer during the conduct of the study, and other funds from Lilly, Pfizer, and Gilead outside of the study. JIV reports personal fees from Syneos Health Clinical Solutions during the conduct of the study. MS has received personal fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Fujifilm, Galapagos, Gilead, Merck, Lilly, Novartis, Pfizer, Regeneron, Samsung, and Sanofi during the conduct of the study. EB has received personal fees from Abbott, Bayer, Boehringer Ingelheim, Servier, and Berlin-Chemie Menarini. RA has received grants from Amgen and Pfizer. RA has also received consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Boehringer Ingelheim, Galapagos, FKB, Gilead, Lilly, UCB, and Novartis. WP, ECEK, HK, MK, and ED declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Smolen JS, Landewé R, Bijlsma J, Burmester G, Chatzidionysiou K, Dougados M, et al. EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis. 2017;76:960–977. doi: 10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-210715. - DOI - PubMed
-
- US Food & Drug Administration. BLA application number 125057: approval letter. https://www.accessdata.fda.gov/drugsatfda_docs/nda/2002/BLA_125057_S000_HUMIRA_A.... Accessed 1 Aug 2019.
-
- AbbVie Inc. Humira® summary of product characteristics. http://www.ema.europa.eu/docs/en_GB/document_library/EPAR_-_Product_Info.... Accessed 1 Aug 2019.
-
- AbbVie Inc. Humira® prescribing information. http://www.rxabbvie.com/pdf/humira.pdf. Accessed 15 Aug 2019.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

