Apolipoprotein B, Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins, and Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Persons with CKD
- PMID: 31831577
- PMCID: PMC6946066
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.07320619
Apolipoprotein B, Triglyceride-Rich Lipoproteins, and Risk of Cardiovascular Events in Persons with CKD
Abstract
Background and objectives: Triglyceride-rich lipoproteins may contribute to the high cardiovascular risk of patients with CKD. This study evaluated associations of apo-B and markers of triglyceride-rich lipoproteins with cardiovascular events in people with CKD.
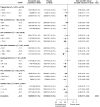
Design, setting, participants, & measurements: Analyses were conducted in 9270 participants with CKD in the Study of Heart and Renal Protection (SHARP): 6245 not on dialysis (mean eGFR 26.5 ml/min per 1.73 m2), and 3025 on dialysis when recruited. Cox regression methods were used to evaluate associations of lipids with incident atherosclerotic and nonatherosclerotic vascular events, adjusting for demographics and clinical characteristics. Hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated per 1 SD higher level for apo-B, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, triglyceride-rich lipoprotein cholesterol (i.e., total cholesterol minus LDL cholesterol minus HDL cholesterol), non-HDL cholesterol, log triglyceride, and log ratio of triglyceride to HDL cholesterol.
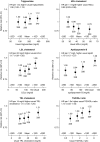
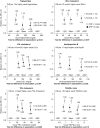
Results: During a median follow-up of 4.9 years (interquartile range, 4.0-5.5 years), 1406 participants experienced at least one atherosclerotic vascular event. In multivariable adjusted models, positive associations with atherosclerotic vascular events were observed for apo-B (HR per 1 SD, 1.19; 95% confidence interval, 1.12 to 1.27), triglycerides (1.06; 1.00 to 1.13), the ratio of triglyceride to HDL cholesterol (1.10; 1.03 to 1.18), and triglyceride-rich lipoprotein cholesterol (1.14; 1.05 to 1.25). By contrast, inverse associations with nonatherosclerotic vascular events were observed for each of these lipid markers: apo-B (HR per 1 SD, 0.92; 0.85 to 0.98), triglycerides (0.86; 0.81 to 0.92), the ratio of triglyceride to HDL cholesterol (0.88; 0.82 to 0.94), and triglyceride-rich lipoprotein cholesterol (0.85; 0.77 to 0.94).
Conclusions: Higher apo-B, triglycerides, ratio of triglyceride to HDL cholesterol, and triglyceride-rich lipoprotein cholesterol concentrations were associated with increased risk of atherosclerotic vascular events in CKD. Reducing triglyceride-rich lipoproteins using novel therapeutic agents could potentially lower the risk of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk in the CKD population.
Keywords: HDL cholesterol; LDL cholesterol; apolipoproteins; cardiovascular disease; cardiovascular diseases; cholesterol; chronic kidney disease; chronic renal insufficiency; demography; follow-up studies; glomerular filtration rate; humans; lipids; lipoprotein cholesterol; lipoprotein triglyceride; lipoproteins; low density lipoprotein triglyceride; renal dialysis; risk factors; triglycerides.
Copyright © 2020 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Lipids and Cardiovascular Risk with CKD.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020 Jan 7;15(1):5-7. doi: 10.2215/CJN.13531119. Epub 2019 Dec 12. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2020. PMID: 31846933 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Saran R, Robinson B, Abbott KC, Agodoa LYC, Bhave N, Bragg-Gresham J, Balkrishnan R, Dietrich X, Eckard A, Eggers PW, Gaipov A, Gillen D, Gipson D, Hailpern SM, Hall YN, Han Y, He K, Herman W, Heung M, Hirth RA, Hutton D, Jacobsen SJ, Jin Y, Kalantar-Zadeh K, Kapke A, Kovesdy CP, Lavallee D, Leslie J, McCullough K, Modi Z, Molnar MZ, Montez-Rath M, Moradi H, Morgenstern H, Mukhopadhyay P, Nallamothu B, Nguyen DV, Norris KC, O'Hare AM, Obi Y, Park C, Pearson J, Pisoni R, Potukuchi PK, Rao P, Repeck K, Rhee CM, Schrager J, Schaubel DE, Selewski DT, Shaw SF, Shi JM, Shieu M, Sim JJ, Soohoo M, Steffick D, Streja E, Sumida K, Tamura MK, Tilea A, Tong L, Wang D, Wang M, Woodside KJ, Xin X, Yin M, You AS, Zhou H, Shahinian V: US renal data system 2017 annual data report: Epidemiology of kidney disease in the United States. Am J Kidney Dis 71[Suppl 1]: A7, 2018 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baigent C, Landray MJ, Reith C, Emberson J, Wheeler DC, Tomson C, Wanner C, Krane V, Cass A, Craig J, Neal B, Jiang L, Hooi LS, Levin A, Agodoa L, Gaziano M, Kasiske B, Walker R, Massy ZA, Feldt-Rasmussen B, Krairittichai U, Ophascharoensuk V, Fellström B, Holdaas H, Tesar V, Wiecek A, Grobbee D, de Zeeuw D, Grönhagen-Riska C, Dasgupta T, Lewis D, Herrington W, Mafham M, Majoni W, Wallendszus K, Grimm R, Pedersen T, Tobert J, Armitage J, Baxter A, Bray C, Chen Y, Chen Z, Hill M, Knott C, Parish S, Simpson D, Sleight P, Young A, Collins R; SHARP Investigators : The effects of lowering LDL cholesterol with simvastatin plus ezetimibe in patients with chronic kidney disease (Study of Heart and Renal Protection): A randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 377: 2181–2192, 2011 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nordestgaard BG, Varbo A: Triglycerides and cardiovascular disease. Lancet 384: 626–635, 2014 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

