MicroRNA-760 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer development via inhibiting G-protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting protein-1 transcription
- PMID: 31832002
- PMCID: PMC6906209
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v25.i45.6619
MicroRNA-760 acts as a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer development via inhibiting G-protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting protein-1 transcription
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer (GC) has become a serious threat to people's health. Accumulative evidence reveals that dysregulation of numerous microRNAs (miRNAs) has been found during malignant formation. So far, the role of microRNA-760 (miR-760) in the development of GC is largely unknown.
Aim: To measure the expression level of miR-760 in GC and investigate its role in gastric tumorigenesis.
Methods: Real-time quantitative polymerase chain reaction and Western blot analysis were used to measure the expression of miR-760 and G-protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting protein-1 (GIT1). Cell growth was detected by 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) and cell colony formation assays. Apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometric analysis. The relationship between miR-760 and GIT1 was verified by luciferase reporter assay.
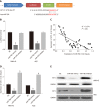
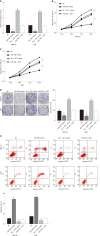
Results: The results showed that the expression of miR-760 was decreased in GC and associated with poor clinical outcomes in GC patients. Furthermore, miR-760 restrained cell proliferation and cell colony formation and induced apoptosis in GC cells. In addition, miR-760 directly targeted GIT1 and negatively regulated its expression in GC. GIT1 was upregulated in GC and predicted a worse prognosis in GC patients. We also found that upregulation of GIT1 weakened the inhibitory effect of miR-760 in GC.
Conclusion: In conclusion, miR-760 targets GIT1 to inhibit cell growth and promote apoptosis in GC cells. Our data demonstrate that miR-760 may be a potential target for the treatment of GC.
Keywords: G-protein-coupled receptor kinase interacting protein-1; Gastric cancer; Invasion; MicroRNA-760; Migration; Proliferation.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

