Enhanced osteopontin splicing regulated by RUNX2 is HDAC-dependent and induces invasive phenotypes in NSCLC cells
- PMID: 31832019
- PMCID: PMC6873507
- DOI: 10.1186/s12935-019-1033-5
Enhanced osteopontin splicing regulated by RUNX2 is HDAC-dependent and induces invasive phenotypes in NSCLC cells
Abstract
Background: Increased cell mobility is a signature when tumor cells undergo epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. TGF-β is a key stimulating factor to promote the transcription of a variety of downstream genes to accelerate cancer progression and metastasis, including osteopontin (OPN) which exists in several functional forms as different splicing variants. In non-small cell lung cancer cells, although increased total OPN expression was observed under various EMT conditions, the exact constitution and the underlining mechanism towards the generation of such OPN splicing isoforms was poorly understood.
Methods: We investigated the possible mechanisms of osteopontin splicing variant and its role in EMT and cancer metastasis using NSCLC cell line and cell and molecular biology techniques.
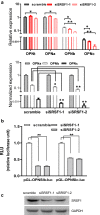
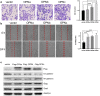
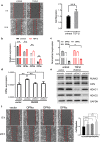
Results: In this study, we determined that OPNc, an exon 4 excluded shorter form of Opn gene products, appeared to be more potent to promote cell invasion. The expression of OPNc was selectively increased to higher abundance during EMT following TGF-β induction. The switching from OPNa to OPNc could be enhanced by RUNX2 (a transcription factor that recognizes the Opn gene promoter) overexpression, but appeared to be strictly in a HDAC dependent manner in A549 cells. The results suggested the increase of minor splicing variant of OPNc required both (1) the enhanced transcription from its coding gene driven by specific transcription factors; and (2) the simultaneous modulation or fluctuation of the coupled splicing process that depends to selective classed of epigenetic regulators, predominately HDAC family members.
Conclusion: Our study not only emphasized the importance of splicing variant for its role in EMT and cancer metastasis, but also helped to understand the possible mechanisms of the epigenetic controls for defining the levels and kinetic of gene splicing isoforms and their generations.
Keywords: EMT; HDAC; OPN; RUNX2; Splicing.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsThe authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functional heterogeneity of osteopontin isoforms in non-small cell lung cancer.J Thorac Oncol. 2010 Oct;5(10):1516-23. doi: 10.1097/JTO.0b013e3181eba6bd. J Thorac Oncol. 2010. PMID: 20689445 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic regulation of osteopontin splicing isoform c defines its role as a microenvironmental factor to promote the survival of colon cancer cells from 5-FU treatment.Cancer Cell Int. 2020 Sep 14;20:452. doi: 10.1186/s12935-020-01541-z. eCollection 2020. Cancer Cell Int. 2020. PMID: 32944000 Free PMC article.
-
Both osteopontin-c and osteopontin-b splicing isoforms exert pro-tumorigenic roles in prostate cancer cells.Prostate. 2012 Nov;72(15):1688-99. doi: 10.1002/pros.22523. Epub 2012 Apr 11. Prostate. 2012. PMID: 22495819
-
Human osteopontin splicing isoforms: known roles, potential clinical applications and activated signaling pathways.Cancer Lett. 2013 Apr 30;331(1):11-7. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2012.12.003. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Cancer Lett. 2013. PMID: 23246372 Review.
-
Osteopontin Expression in Thyroid Cancer: Deciphering EMT-Related Molecular Mechanisms.Biomedicines. 2021 Oct 1;9(10):1372. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9101372. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34680488 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Signaling pathways and clinical application of RASSF1A and SHOX2 in lung cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020 Jun;146(6):1379-1393. doi: 10.1007/s00432-020-03188-9. Epub 2020 Apr 7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32266538 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The microRNA-130a-5p/RUNX2/STK32A network modulates tumor invasive and metastatic potential in non-small cell lung cancer.BMC Cancer. 2020 Jun 22;20(1):580. doi: 10.1186/s12885-020-07056-0. BMC Cancer. 2020. Retraction in: BMC Cancer. 2025 Jul 22;25(1):1198. doi: 10.1186/s12885-025-14700-0. PMID: 32571328 Free PMC article. Retracted.
-
Roles of Histone Acetylation Modifiers and Other Epigenetic Regulators in Vascular Calcification.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 4;21(9):3246. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093246. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32375326 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Meta-analysis of Osteopontin splice variants in cancer.BMC Cancer. 2023 Apr 24;23(1):373. doi: 10.1186/s12885-023-10854-x. BMC Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37095438 Free PMC article.
-
Chromatin and Cancer: Implications of Disrupted Chromatin Organization in Tumorigenesis and Its Diversification.Cancers (Basel). 2023 Jan 11;15(2):466. doi: 10.3390/cancers15020466. Cancers (Basel). 2023. PMID: 36672415 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Smith RA, Andrews KS, Brooks D, Fedewa SA, Manassaram-Baptiste D, Saslow D, Brawley OW, Wender RC. Cancer screening in the United States, 2018: a review of current American Cancer Society guidelines and current issues in cancer screening. CA Cancer J Clin. 2018;684:297–316. doi: 10.3322/caac.21446. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

