Overview of organic anion transporters and organic anion transporter polypeptides and their roles in the liver
- PMID: 31832394
- PMCID: PMC6906560
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3915
Overview of organic anion transporters and organic anion transporter polypeptides and their roles in the liver
Abstract
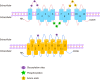
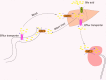
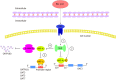
Organic anion transporters (OATs) and organic anion transporter polypeptides (OATPs) are classified within two SLC superfamilies, namely, the SLC22A superfamily and the SLCO superfamily (formerly the SLC21A family), respectively. They are expressed in many tissues, such as the liver and kidney, and mediate the absorption and excretion of many endogenous and exogenous substances, including various drugs. Most are composed of 12 transmembrane polypeptide chains with the C-terminus and the N-terminus located in the cell cytoplasm. OATs and OATPs are abundantly expressed in the liver, where they mainly promote the uptake of various endogenous substrates such as bile acids and various exogenous drugs such as antifibrotic and anticancer drugs. However, differences in the locations of glycosylation sites, phosphorylation sites, and amino acids in the OAT and OATP structures lead to different substrates being transported to the liver, which ultimately results in their different roles in the liver. To date, few articles have addressed these aspects of OAT and OATP structures, and we study further the similarities and differences in their structures, tissue distribution, substrates, and roles in liver diseases.
Keywords: Liver cancer; Liver cirrhosis; Liver fibrosis; Organic anion; Substrate transport; Targeted therapy.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No potential conflicts of interest exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
OATPs, OATs and OCTs: the organic anion and cation transporters of the SLCO and SLC22A gene superfamilies.Br J Pharmacol. 2012 Mar;165(5):1260-87. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01724.x. Br J Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22013971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Trafficking and other regulatory mechanisms for organic anion transporting polypeptides and organic anion transporters that modulate cellular drug and xenobiotic influx and that are dysregulated in disease.Br J Pharmacol. 2017 Jul;174(13):1908-1924. doi: 10.1111/bph.13785. Epub 2017 Apr 24. Br J Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28299773 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Organic anion transporting polypeptides of the OATP/ SLC21 family: phylogenetic classification as OATP/ SLCO superfamily, new nomenclature and molecular/functional properties.Pflugers Arch. 2004 Feb;447(5):653-65. doi: 10.1007/s00424-003-1168-y. Epub 2003 Oct 25. Pflugers Arch. 2004. PMID: 14579113 Review.
-
Post-translational regulation of the major drug transporters in the families of organic anion transporters and organic anion-transporting polypeptides.J Biol Chem. 2020 Dec 11;295(50):17349-17364. doi: 10.1074/jbc.REV120.009132. Epub 2020 Oct 13. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 33051208 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Critical domains within the sequence of human organic anion transporting polypeptides.Curr Drug Metab. 2014 Mar;15(3):265-70. doi: 10.2174/1389200214666131229111118. Curr Drug Metab. 2014. PMID: 24372098 Review.
Cited by
-
Liver transcriptome profiling and functional analysis of intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR) piglets reveals a genetic correction and sexual-dimorphic gene expression during postnatal development.BMC Genomics. 2020 Oct 8;21(1):701. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07094-9. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33032518 Free PMC article.
-
Indoxyl-Sulfate-Induced Redox Imbalance in Chronic Kidney Disease.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;10(6):936. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060936. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207816 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Researches on the evaluation of pesticide safety in humans using a pharmacokinetic approach.J Pestic Sci. 2021 Aug 20;46(3):290-296. doi: 10.1584/jpestics.J21-02. J Pestic Sci. 2021. PMID: 34566464 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Prognostic Organic Cation and Anion Transporters in Different Cancer Entities by In Silico Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 24;21(12):4491. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124491. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32599841 Free PMC article.
-
Gadoxetate-Enhanced MRI as a Diagnostic Tool in the Management of Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Report from a 2020 Asia-Pacific Multidisciplinary Expert Meeting.Korean J Radiol. 2022 Jul;23(7):697-719. doi: 10.3348/kjr.2021.0593. Epub 2022 May 9. Korean J Radiol. 2022. PMID: 35555884 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hagenbuch B, Meier PJ. Organic anion transporting polypeptides of the OATP/ SLC21 family: phylogenetic classification as OATP/ SLCO superfamily, new nomenclature and molecular/functional properties. Pflugers Arch. 2004;447:653–665. - PubMed
-
- Shitara Y, Horie T, Sugiyama Y. Transporters as a determinant of drug clearance and tissue distribution. Eur J Pharm Sci. 2006;27:425–446. - PubMed
-
- Meier PJ. Molecular mechanisms of hepatic bile salt transport from sinusoidal blood into bile. Am J Physiol. 1995;269:G801–G812. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

