Value of early diagnosis of sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury by renal contrast-enhanced ultrasound
- PMID: 31832395
- PMCID: PMC6906561
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3934
Value of early diagnosis of sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury by renal contrast-enhanced ultrasound
Abstract
Background: The incidence of acute kidney injury (AKI) in patients with sepsis is high, and the prognosis of patients with septic AKI is poor. The early diagnosis and treatment of septic AKI is of great significance in improving the prognosis of patients with sepsis.
Aim: To explore the value of contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS), serum creatinine (Scr), and other indicators in the early diagnosis of septic AKI.
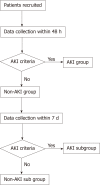
Methods: Ninety patients with sepsis during hospitalization at Tongji Hospital of Tongji University were recruited as subjects. Each patient was recorded with relevant basic data, clinical indicators, and CEUS results. The patients were divided into AKI group and non-AKI group according to the results of renal function diagnosis after 48 h. On the 7th day, the renal function of the non-AKI group was re-evaluated and the patients were further divided into AKI subgroup and non-AKI subgroup. The differences of the indicators in different groups were compared, and the diagnostic value of each indicator and their combination for septic AKI was analyzed.
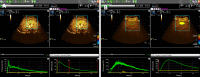
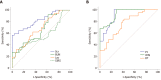
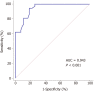
Results: Systemic inflammatory response score (2.58 ± 0.75), blood lactic acid (3.01 ± 1.33 mmol/L), Scr (141.82 ± 27.19 μmol/L), blood urea nitrogen (4.41 ± 0.81mmol/L), and rise time (10.23 ± 2.63 s) in the AKI group were higher than those in the non-AKI group. Peak intensity (PI) (10.78 ± 3.98 dB) and wash in slope (WIS) (1.07 ± 0.53 dB/s) were lower than those in the non-AKI group. The differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The PI (12.83 ± 3.77 dB) and WIS (1.22 ± 0.68 dB/s) in the AKI subgroup were lower than those in the non-AKI subgroup, and the differences were statistically significant (P < 0.05). The area under curve (AUC) of Scr for the diagnosis of septic AKI was 0.825 with a sensitivity of 56.76% and a specificity of 100%. The AUCs of WIS and PI (0.928 and 0.912) were higher than those of Scr. Their sensitivities were 100%, but the specificities were 71.70% and 75.47%. The AUC of the combination of three indicators for the diagnosis of septic AKI was 0.943, which was significantly higher than the AUC diagnosed by each single indicator. The sensitivity was 94.59%, and the specificity was 81.13%.
Conclusion: The combination of Scr, PI, and WIS can improve the diagnostic accuracy of septic AKI. PI and WIS are expected to predict the occurrence of early septic AKI.
Keywords: Acute kidney injury; Contrast-enhanced ultrasound; Peak intensity; Sepsis; Serum creatinine; Wash in slope.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) and Ultra-Microangiography (UMA) in Critically Ill Children with Acute Kidney Injury.Children (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;11(10):1205. doi: 10.3390/children11101205. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Continuous contrast-enhanced ultrasound applied to acute kidney injury caused by sepsis: a diagnostic clinical study].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018 Feb;30(2):160-164. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2018.02.013. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2018. PMID: 29402367 Chinese.
-
[Early diagnostic value of neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin and interleukin-18 in patients with sepsis-induced acute kidney injury].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016 Aug;28(8):718-22. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2016.08.010. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2016. PMID: 27434563 Chinese.
-
Early Diagnostic Value of Urinary NGAL in Acute Kidney Injury in Septic Patients.Altern Ther Health Med. 2022 Oct;28(7):120-124. Altern Ther Health Med. 2022. PMID: 35751900
-
A pilot trial to evaluate the clinical usefulness of contrast-enhanced ultrasound in predicting renal outcomes in patients with acute kidney injury.PLoS One. 2020 Jun 24;15(6):e0235130. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0235130. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32579595 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Decreased renal cortical perfusion, independent of changes in renal blood flow and sublingual microcirculatory impairment, is associated with the severity of acute kidney injury in patients with septic shock.Crit Care. 2022 Sep 1;26(1):261. doi: 10.1186/s13054-022-04134-6. Crit Care. 2022. PMID: 36050737 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluating renal microcirculation in patients with acute kidney injury by contrast-enhanced ultrasonography: a protocol for an observational cohort study.BMC Nephrol. 2022 Dec 8;23(1):392. doi: 10.1186/s12882-022-03021-0. BMC Nephrol. 2022. PMID: 36482379 Free PMC article.
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound (CEUS) and Ultra-Microangiography (UMA) in Critically Ill Children with Acute Kidney Injury.Children (Basel). 2024 Sep 30;11(10):1205. doi: 10.3390/children11101205. Children (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457170 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ultrasonographic assessment of renal microcirculation is a new vision for the treatment of intensive care unit associated acute kidney injury.Eur J Med Res. 2024 Feb 10;29(1):115. doi: 10.1186/s40001-024-01704-y. Eur J Med Res. 2024. PMID: 38341556 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Predictive Value of the Transthoracic Echocardiography Index for Acute Kidney Injury after Cardiac Valve Surgery.J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022 Sep 21;9(10):316. doi: 10.3390/jcdd9100316. J Cardiovasc Dev Dis. 2022. PMID: 36286268 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tandon P, Garcia-Tsao G. Bacterial infections, sepsis, and multiorgan failure in cirrhosis. Semin Liver Dis. 2008;28:26–42. - PubMed
-
- Spapen H. Liver perfusion in sepsis, septic shock, and multiorgan failure. Anat Rec (Hoboken) 2008;291:714–720. - PubMed
-
- Carcillo JA, Halstead ES, Hall MW, Nguyen TC, Reeder R, Aneja R, Shakoory B, Simon D Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development Collaborative Pediatric Critical Care Research Network Investigators. Three Hypothetical Inflammation Pathobiology Phenotypes and Pediatric Sepsis-Induced Multiple Organ Failure Outcome. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2017;18:513–523. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

