Fatal complications in a patient with severe multi-space infections in the oral and maxillofacial head and neck regions: A case report
- PMID: 31832421
- PMCID: PMC6906581
- DOI: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.4150
Fatal complications in a patient with severe multi-space infections in the oral and maxillofacial head and neck regions: A case report
Abstract
Background: Odontogenic infection is one of the common infectious diseases in oral and maxillofacial head and neck regions. Clinically, if early odontogenic infections such as acute periapical periodontitis, alveolar abscess, and pericoronitis of wisdom teeth are not treated timely, effectively and correctly, the infected tissue may spread up to the skull and brain, down to the thoracic cavity, abdominal cavity and other areas through the natural potential fascial space in the oral and maxillofacial head and neck. Severe multi-space infections are formed and can eventually lead to life-threatening complications (LTCs), such as intracranial infection, pleural effusion, empyema, sepsis and even death.
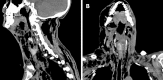
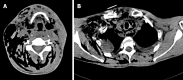
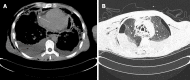
Case summary: We report a rare case of death in a 41-year-old man with severe odontogenic multi-space infections in the oral and maxillofacial head and neck regions. One week before admission, due to pain in the right lower posterior teeth, the patient placed a cigarette butt dipped in the pesticide "Miehailin" into the "dental cavity" to relieve the pain. Within a week, the infection gradually spread bilaterally to the floor of the mouth, submandibular space, neck, chest, waist, back, temporal and other areas. The patient had difficulty breathing, swallowing and eating, and was transferred to our hospital as an emergency admission. Following admission, oral and maxillofacial surgeons immediately organized consultations with doctors in otolaryngology, thoracic surgery, general surgery, hematology, anesthesia and the intensive care unit to assist with treatment. The patient was treated with the highest level of antibiotics (vancomycin) and extensive abscess incision and drainage in the oral, maxillofacial, head and neck, chest and back regions. Unfortunately, the patient died of septic shock and multiple organ failure on the third day after admission.
Conclusion: Odontogenic infection can cause serious multi-space infections in the oral and maxillofacial head and neck regions, which can result in multiple LTCs. The management and treatment of LTCs such as multi-space infections should be multidisciplinary led by oral and maxillofacial surgeons.
Keywords: Case report; Complication; Head and neck; Maxillofacial; Multi-space infections; Odontogenic infection; Oral.
©The Author(s) 2019. Published by Baishideng Publishing Group Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: No conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Application of Disposable Multifunctional Drainage Tube-Assisted Irrigation in Patients With Severe Multi-Space Infections in Oral and Maxillofacial Head and Neck Regions.J Craniofac Surg. 2020 Mar/Apr;31(2):e202-e205. doi: 10.1097/SCS.0000000000006236. J Craniofac Surg. 2020. PMID: 31977712
-
Management of complex multi-space odontogenic infections.J Tenn Dent Assoc. 2002 Fall;82(3):39-47. J Tenn Dent Assoc. 2002. PMID: 12572406
-
Odontogenic Orofacial Space Infections.2023 Jul 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2023 Jul 12. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 36943966 Free Books & Documents.
-
Update on Antimicrobial Therapy in Management of Acute Odontogenic Infection in Oral and Maxillofacial Surgery.Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2022 Feb;34(1):169-177. doi: 10.1016/j.coms.2021.08.005. Epub 2021 Oct 30. Oral Maxillofac Surg Clin North Am. 2022. PMID: 34728145 Review.
-
Odontogenic cervico-fascial infections: a continuing threat.J Ir Dent Assoc. 2013 Dec-2014 Jan;59(6):301-7. J Ir Dent Assoc. 2013. PMID: 24575614 Review.
Cited by
-
Evaluating the risk factors for complications of patients with oral and maxillofacial space infections: a systematic review and meta-analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Jul 5;25(1):1115. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-06521-1. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40618092 Free PMC article.
-
Fascial space odontogenic infections: Ultrasonography as an alternative to magnetic resonance imaging.World J Clin Cases. 2021 Jan 26;9(3):573-580. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v9.i3.573. World J Clin Cases. 2021. PMID: 33553395 Free PMC article.
-
Maxillofacial space infection experience and risk factors: a retrospective study of 222 cases.Ir J Med Sci. 2021 Aug;190(3):1045-1053. doi: 10.1007/s11845-020-02431-z. Epub 2020 Nov 14. Ir J Med Sci. 2021. PMID: 33188628
-
Comparison of the efficacy of the anterolateral thigh flap for perforator localization in the repair of head and neck soft tissue defects patients: A protocol study for a randomized controlled trial.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Dec 11;99(50):e23080. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000023080. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 33327231 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Negative pressure sealing drainage technology combined with adequate irrigation for oral and maxillofacial space infection can improve serum inflammatory factor levels.Am J Transl Res. 2023 Nov 15;15(11):6605-6612. eCollection 2023. Am J Transl Res. 2023. PMID: 38074802 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maroldi R, Farina D, Ravanelli M, Lombardi D, Nicolai P. Emergency imaging assessment of deep neck space infections. Semin Ultrasound CT MR. 2012;33:432–442. - PubMed
-
- Wills PI, Vernon RP., Jr Complications of space infections of the head and neck. Laryngoscope. 1981;91:1129–1136. - PubMed
-
- Larawin V, Naipao J, Dubey SP. Head and neck space infections. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;135:889–893. - PubMed
-
- Huang L, Jiang B, Cai X, Zhang W, Qian W, Li Y, Guan X, Liang X, Zhou L, Zhu J, Zhang Z. Multi-Space Infections in the Head and Neck: Do Underlying Systemic Diseases Have a Predictive Role in Life-Threatening Complications? J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2015;73:1320.e1–1320.10. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

