Clinical Implications of Microbiologic Treatment Failure in the Setting of Clinical Cure of Bacterial Pneumonia
- PMID: 31832641
- PMCID: PMC7819508
- DOI: 10.1093/cid/ciz1187
Clinical Implications of Microbiologic Treatment Failure in the Setting of Clinical Cure of Bacterial Pneumonia
Abstract
Background: Microbiologic cure is a common outcome in pneumonia clinical trials, but its clinical significance is incompletely understood.
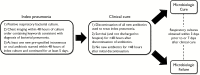
Methods: We conducted a retrospective cohort study of adult patients hospitalized with bacterial pneumonia who achieved clinical cure. Rates of recurrent pneumonia and death were compared between patients with persistent growth of the index pathogen at the time of clinical cure (microbiologic failure) and those with pathogen eradication (microbiologic cure).
Results: Among 441 patients, 237 experienced microbiologic cure and 204 experienced microbiologic failure. Prevalences of comorbidities, ventilator dependence, and severity of acute illness were similar between groups. Patients with microbiologic failure experienced significantly higher rates of recurrent pneumonia or death following clinical cure than patients with microbiologic cure, controlling for comorbid conditions, severity of acute illness, appropriateness of empiric antibiotics, intensive care unit placement, tracheostomy dependence, and immunocompromised status (90-day multivariable adjusted odds ratio [OR], 1.56; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.04-2.35). This association was observed among patients with pneumonias caused by Staphylococcus aureus (90-day multivariable adjusted OR, 3.69; 95% CI, 1.73-7.90). A trend was observed among pneumonias caused by nonfermenting gram-negative bacilli, but not Enterobacteriaceae or other pathogens.
Conclusions: Microbiologic treatment failure was independently associated with recurrent pneumonia or death among patients with bacterial pneumonia following clinical cure. Microbiologic cure merits further study as a metric to guide therapeutic interventions for patients with bacterial pneumonia.
Keywords: hospital-acquired pneumonia; pneumonia; severe community-acquired pneumonia; ventilator-associated pneumonia.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press for the Infectious Diseases Society of America. All rights reserved. For permissions, e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
Comment in
-
Microbiologic Failure Despite Clinical Cure in Pneumonia: Cum Hoc and Post Hoc Ergo Propter Hoc.Clin Infect Dis. 2020 Dec 15;71(12):3042-3043. doi: 10.1093/cid/ciz1191. Clin Infect Dis. 2020. PMID: 31832646 No abstract available.
References
-
- Melsen WG, Rovers MM, Groenwold RH, et al. Attributable mortality of ventilator-associated pneumonia: a meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised prevention studies. Lancet Infect Dis 2013; 13:665–71. - PubMed
-
- Sopena N, Sabrià M; Neunos 2000 Study Group Multicenter study of hospital-acquired pneumonia in non-ICU patients. Chest 2005; 127:213–9. - PubMed
-
- Siempos II, Athanassa Z, Falagas ME. Frequency and predictors of ventilator-associated pneumonia recurrence: a meta-analysis. Shock 2008; 30:487–95. - PubMed