Quantitative analysis of vitamin D and its main metabolites in human milk by supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry
- PMID: 31832707
- PMCID: PMC6992569
- DOI: 10.1007/s00216-019-02248-5
Quantitative analysis of vitamin D and its main metabolites in human milk by supercritical fluid chromatography coupled to tandem mass spectrometry
Abstract
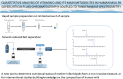
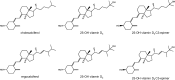
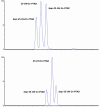
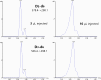
A novel method to quantitate vitamin D and its main metabolites (vitamin D3, vitamin D2, and their 25-hydroxy metabolites) in breast milk by supercritical fluid chromatography has been developed and fully validated. A small volume of sample (1 mL) is subjected to ethanolic protein precipitation and liquid-liquid extraction. Final extracts are derivatized with 4-phenyl-1,2,4-triazoline-3,5-dione and vitamin D derivatives analyzed by supercritical fluid chromatography hyphenated to tandem mass spectrometry with atmospheric pressure chemical ionization. Multiple reaction monitoring is used for quantitation. Separation conditions were optimized using a gradient of methanol-water-ammonium formate into carbon dioxide. Make-up solvent was methanol containing ammonium formate. The quantitation limit reached levels as low as 50 pmol/L, with intra- and inter-day relative standard deviations lower than 15% and 20% for all analytes. Accuracy was evaluated by spiking experiments and was well within acceptability ratios (± 15%). The method was then applied to a subset of commercially available human milk samples. The newly developed method provides opportunities to determine the nutritional status of mother-infant dyads from a non-invasive measure, or for interventional or observational studies building knowledge on the composition of human milk. Graphical abstract.
Keywords: Human milk; Supercritical fluid chromatography; Tandem mass spectrometry; Vitamin D.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

