Platform-integrated mRNA isoform quantification
- PMID: 31834359
- PMCID: PMC7178424
- DOI: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btz932
Platform-integrated mRNA isoform quantification
Abstract
Motivation: Accurate estimation of transcript isoform abundance is critical for downstream transcriptome analyses and can lead to precise molecular mechanisms for understanding complex human diseases, like cancer. Simplex mRNA Sequencing (RNA-Seq) based isoform quantification approaches are facing the challenges of inherent sampling bias and unidentifiable read origins. A large-scale experiment shows that the consistency between RNA-Seq and other mRNA quantification platforms is relatively low at the isoform level compared to the gene level. In this project, we developed a platform-integrated model for transcript quantification (IntMTQ) to improve the performance of RNA-Seq on isoform expression estimation. IntMTQ, which benefits from the mRNA expressions reported by the other platforms, provides more precise RNA-Seq-based isoform quantification and leads to more accurate molecular signatures for disease phenotype prediction.
Results: In the experiments to assess the quality of isoform expression estimated by IntMTQ, we designed three tasks for clustering and classification of 46 cancer cell lines with four different mRNA quantification platforms, including newly developed NanoString's nCounter technology. The results demonstrate that the isoform expressions learned by IntMTQ consistently provide more and better molecular features for downstream analyses compared with five baseline algorithms which consider RNA-Seq data only. An independent RT-qPCR experiment on seven genes in twelve cancer cell lines showed that the IntMTQ improved overall transcript quantification. The platform-integrated algorithms could be applied to large-scale cancer studies, such as The Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA), with both RNA-Seq and array-based platforms available.
Availability and implementation: Source code is available at: https://github.com/CompbioLabUcf/IntMTQ.
Supplementary information: Supplementary data are available at Bioinformatics online.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Figures
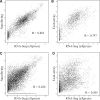
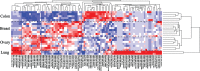
References
-
- Bray N.L. et al. (2016) Near-optimal probabilistic RNA-seq quantification. Nat. Biotechnol., 34, 525–527. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

