The Quest for Phenolic Compounds from Macroalgae: A Review of Extraction and Identification Methodologies
- PMID: 31835386
- PMCID: PMC6995553
- DOI: 10.3390/biom9120847
The Quest for Phenolic Compounds from Macroalgae: A Review of Extraction and Identification Methodologies
Abstract
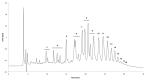
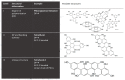
The current interest of the scientific community for the exploitation of high-value compounds from macroalgae is related to the increasing knowledge of their biological activities and health benefits. Macroalgae phenolic compounds, particularly phlorotannins, have gained particular attention due to their specific bioactivities, including antioxidant, antiproliferative, or antidiabetic. Notwithstanding, the characterization of macroalgae phenolic compounds is a multi-step task, with high challenges associated with their isolation and characterization, due to the highly complex and polysaccharide-rich matrix of macroalgae. Therefore, this fraction is far from being fully explored. In fact, a critical revision of the extraction and characterization methodologies already used in the analysis of phenolic compounds from macroalgae is lacking in the literature, and it is of uttermost importance to compile validated methodologies and discourage misleading practices. The aim of this review is to discuss the state-of-the-art of phenolic compounds already identified in green, red, and brown macroalgae, reviewing their structural classification, as well as critically discussing extraction methodologies, chromatographic separation techniques, and the analytical strategies for their characterization, including information about structural identification techniques and key spectroscopic profiles. For the first time, mass spectrometry data of phlorotannins, a chemical family quite exclusive of macroalgae, is compiled and discussed.
Keywords: bioactive compounds; characterization; extraction; macroalgae; mass spectrometry; phenolic compounds; phlorotannins; seaweed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Del Rio D., Rodriguez-Mateos A., Spencer J.P.E., Tognolini M., Borges G., Crozier A. Dietary (Poly)phenolics in Human Health: Structures, Bioavailability, and Evidence of Protective Effects Against Chronic Diseases. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2012;18:1818–1892. doi: 10.1089/ars.2012.4581. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Uysal S., Aktumsek A., Picot-Allain C.M.N., Unuvar H., Mollica A., Georgiev M.I., Zengin G., Mahomoodally M.F. Biological, chemical and in silico fingerprints of Dianthus calocephalus Boiss.: A novel source for rutin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018;113:179–186. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2018.01.049. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Santos S.A.O., Vilela C., Freire C.S.R., Neto C.P., Silvestre A.J.D. Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry applied to the identification of valuable phenolic compounds from eucalyptus wood. J. Chromatogr. B. 2013;938:65–74. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.08.034. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Gupta S., Abu-Ghannam N. Bioactive potential and possible health effects of edible brown seaweeds. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2011;22:315–326. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2011.03.011. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

