B Cell Abnormalities in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis-Role in Pathogenesis and Effect of Immunosuppressive Treatments
- PMID: 31835612
- PMCID: PMC6940927
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20246231
B Cell Abnormalities in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Lupus Nephritis-Role in Pathogenesis and Effect of Immunosuppressive Treatments
Abstract
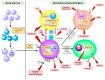
Abnormalities in B cells play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis (LN). Breach in central and peripheral tolerance mechanisms generates autoreactive B cells which contribute to the pathogenesis of SLE and LN. Dysregulation of B cell transcription factors, cytokines and B cell-T cell interaction can result in aberrant B cell maturation and autoantibody production. These immunological abnormalities also lead to perturbations in circulating and infiltrating B cells in SLE and LN patients. Conventional and novel immunosuppressive medications confer differential effects on B cells which have important clinical implications. While cyclophosphamide and mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) showed comparable clinical efficacy in active LN, MMF induction was associated with earlier reduction in circulating plasmablasts and plasma cells. Accumulating evidence suggests that MMF maintenance is associated with lower risk of disease relapse than azathioprine, which may be explained by its more potent and selective suppression of B cell proliferation. Novel therapeutic approaches targeting the B cell repertoire include B cell depletion with monoclonal antibodies binding to cell surface markers, inhibition of B cell cytokines, and modulation of costimulatory signals in B cell-T cell interaction. These biologics, despite showing improvements in serological parameters and proteinuria, did not achieve primary endpoints when used as add-on therapy to standard treatments in active LN patients. Other emerging treatments such as calcineurin inhibitors, mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors and proteasome inhibitors also show distinct inhibitory effects on the B cell repertoire. Advancement in the knowledge on B cell biology has fueled the development of new therapeutic strategies in SLE and LN. Modification in background treatments, study endpoints and selective recruitment of subjects showing aberrant B cells or its signaling pathways when designing future clinical trials may better elucidate the roles of these novel therapies for SLE and LN patients.
Keywords: B cell abnormalities; lupus nephritis; pathogenesis; systemic lupus erythematosus; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest
Figures
Similar articles
-
Current status of lupus nephritis.Indian J Med Res. 2017 Feb;145(2):167-178. doi: 10.4103/ijmr.IJMR_163_16. Indian J Med Res. 2017. PMID: 28639592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modern therapeutic strategies for paediatric systemic lupus erythematosus and lupus nephritis.Acta Paediatr. 2010 Jul;99(7):967-74. doi: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.2010.01771.x. Epub 2010 Mar 11. Acta Paediatr. 2010. PMID: 20222881 Review.
-
Calcineurin and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus: The Rationale for Using Calcineurin Inhibitors in the Treatment of Lupus Nephritis.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 27;22(3):1263. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031263. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33514066 Free PMC article. Review.
-
B lymphocytes and lupus nephritis: new insights into pathogenesis and targeted therapies.Kidney Int. 2008 Feb;73(3):261-8. doi: 10.1038/sj.ki.5002663. Epub 2007 Nov 14. Kidney Int. 2008. PMID: 18004299 Review.
-
Mycophenolate mofetil in the treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011 Sep;23(5):454-8. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e328349a1e5. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2011. PMID: 21720247 Review.
Cited by
-
CD52 Is Elevated on B cells of SLE Patients and Regulates B Cell Function.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 4;11:626820. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.626820. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33658999 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory Effects of Diet and Nutrients in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE): A Systematic Review.Front Immunol. 2020 Jul 22;11:1477. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.01477. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32793202 Free PMC article.
-
Termination of CD40L co-stimulation promotes human B cell differentiation into antibody-secreting cells.Eur J Immunol. 2022 Oct;52(10):1662-1675. doi: 10.1002/eji.202249972. Epub 2022 Sep 20. Eur J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36073009 Free PMC article.
-
Baricitinib decreases anti-dsDNA in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from a phase II double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial.Arthritis Res Ther. 2022 May 16;24(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s13075-022-02794-x. Arthritis Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 35578304 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Low positivity rates for HBeAg and HBV DNA in rheumatoid arthritis patients: a case-control study.BMC Infect Dis. 2022 Jun 24;22(1):570. doi: 10.1186/s12879-022-07536-7. BMC Infect Dis. 2022. PMID: 35751011 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical