The Emerging Landscape of p53 Isoforms in Physiology, Cancer and Degenerative Diseases
- PMID: 31835844
- PMCID: PMC6941119
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20246257
The Emerging Landscape of p53 Isoforms in Physiology, Cancer and Degenerative Diseases
Abstract
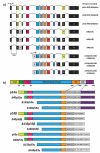
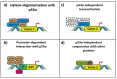
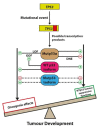
p53, first described four decades ago, is now established as a master regulator of cellular stress response, the "guardian of the genome". p53 contributes to biological robustness by behaving in a cellular-context dependent manner, influenced by several factors (e.g., cell type, active signalling pathways, the type, extent and intensity of cellular damage, cell cycle stage, nutrient availability, immune function). The p53 isoforms regulate gene transcription and protein expression in response to the stimuli so that the cell response is precisely tuned to the cell signals and cell context. Twelve isoforms of p53 have been described in humans. In this review, we explore the interactions between p53 isoforms and other proteins contributing to their established cellular functions, which can be both tumour-suppressive and oncogenic in nature. Evidence of p53 isoform in human cancers is largely based on RT-qPCR expression studies, usually investigating a particular type of isoform. Beyond p53 isoform functions in cancer, it is implicated in neurodegeneration, embryological development, progeroid phenotype, inflammatory pathology, infections and tissue regeneration, which are described in this review.
Keywords: cancer; isoforms; p53; p53 response.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
p53 Isoforms in Cellular Senescence- and Ageing-Associated Biological and Physiological Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Nov 29;20(23):6023. doi: 10.3390/ijms20236023. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31795382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53 and its isoforms in cancer.Br J Cancer. 2007 Aug 6;97(3):277-82. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6603886. Epub 2007 Jul 17. Br J Cancer. 2007. PMID: 17637683 Free PMC article. Review.
-
p53 isoforms - a conspiracy to kidnap p53 tumor suppressor activity?Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Feb;66(3):391-406. doi: 10.1007/s00018-008-8336-3. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 18854945 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biological functions of p53 isoforms through evolution: lessons from animal and cellular models.Cell Death Differ. 2011 Dec;18(12):1815-24. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2011.120. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Cell Death Differ. 2011. PMID: 21941372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The isoforms of the p53 protein.Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010 Mar;2(3):a000927. doi: 10.1101/cshperspect.a000927. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2010. PMID: 20300206 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Δ133p53α enhances metabolic and cellular fitness of TCR-engineered T cells and promotes superior antitumor immunity.J Immunother Cancer. 2021 Jun;9(6):e001846. doi: 10.1136/jitc-2020-001846. J Immunother Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34112738 Free PMC article.
-
The HLA-G immune checkpoint: a new immuno-stimulatory role for the α1-domain-deleted isoform.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022 May 21;79(6):310. doi: 10.1007/s00018-022-04359-2. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35596891 Free PMC article.
-
Altered Expression of Shorter p53 Family Isoforms Can Impact Melanoma Aggressiveness.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Oct 18;13(20):5231. doi: 10.3390/cancers13205231. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34680379 Free PMC article.
-
Activated CD90/Thy-1 fibroblasts co-express the Δ133p53β isoform and are associated with highly inflamed rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2023 Apr 15;25(1):62. doi: 10.1186/s13075-023-03040-8. Arthritis Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37060003 Free PMC article.
-
The Elephant Evolved p53 Isoforms that Escape MDM2-Mediated Repression and Cancer.Mol Biol Evol. 2022 Jul 2;39(7):msac149. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msac149. Mol Biol Evol. 2022. PMID: 35792674 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

