Effects of Dietary Selenium Deficiency or Excess on Selenoprotein Gene Expression in the Spleen Tissue of Pigs
- PMID: 31835880
- PMCID: PMC6940954
- DOI: 10.3390/ani9121122
Effects of Dietary Selenium Deficiency or Excess on Selenoprotein Gene Expression in the Spleen Tissue of Pigs
Abstract
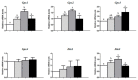
To evaluate the effects of dietary Se deficiency and excess on the mRNA levels of selenoproteins in pig spleen tissues, 20 healthy uncastrated boars (Duroc × Landrace × Yorkshire, 10 ± 0.72 kg) were randomly divided into four groups (5 pigs per group). The pigs were fed a Se deficient corn-soybean basal feed (Se content <0.03 mg/kg) or basal feed with added sodium selenite at 0.3, 1.0, or 3.0 mg Se/kg diet, respectively. The experiment lasted 16 weeks. The spleen tissue was collected to examine the mRNA expression levels of 24 selenoprotein genes at the end of the study. Compared with pigs in other groups, those fed with the 1.0 mg Se/kg diet had higher mRNA levels of glutathione peroxidase 1 (Gpx1), glutathione peroxidase 2 (Gpx2), deiodinase type II (Dio2), thioredoxin reductase 3 (Txnrd3), selenoprotein H (Selh), selenoprotein N, 1 (Sepn1), selenoprotein P1 (Sepp1), and selenoprotein V (Selv) in the spleen (p < 0.05). Dietary Se deficiency resulted in lower mRNA levels of Gpx1, Gpx2, glutathione peroxidase 3 (Gpx3), Dio2, thioredoxin reductase 2 (Txnrd2), Txnrd3, Selh, selenoprotein I (Seli), selenoprotein K (Selk), selenoprotein M (Selm), Sepn1, Sepp1, and Selv in the spleen than the other three groups. Dietary Se levels did not affect the mRNA levels of glutathione peroxidase 4 (Gpx4), deiodinase type I (Dio1), deiodinase type III (Dio3), selenophosphate synthetase 2 (Sephs2), thioredoxin reductase 1 (Txnrd1), selenoprotein O (Selo), selenoprotein S (Sels), selenoprotein W (Selw), selenoprotein X (Selx), and selenoprotein 15 (Sel15) in the spleen (p > 0.05). Dietary Se levels can affect the transcription levels of 14 selenoprotein genes in the spleen of pigs.
Keywords: pig; selenium; selenoprotein; spleen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Selenium deficiency influences nitric oxide and selenoproteins in pancreas of chickens.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014 Dec;161(3):341-9. doi: 10.1007/s12011-014-0139-9. Epub 2014 Oct 16. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2014. PMID: 25319006
-
Selenoprotein Gene Nomenclature.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 11;291(46):24036-24040. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.756155. Epub 2016 Sep 19. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27645994 Free PMC article.
-
Selenium Deficiency Affects the mRNA Expression of Inflammatory Factors and Selenoprotein Genes in the Kidneys of Broiler Chicks.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016 May;171(1):201-7. doi: 10.1007/s12011-015-0512-3. Epub 2015 Sep 23. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2016. PMID: 26400650
-
Selenium, selenoproteins and human health: a review.Public Health Nutr. 2001 Apr;4(2B):593-9. doi: 10.1079/phn2001143. Public Health Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11683552 Review.
-
Responsiveness of selenoproteins to dietary selenium.Annu Rev Nutr. 1999;19:1-16. doi: 10.1146/annurev.nutr.19.1.1. Annu Rev Nutr. 1999. PMID: 10448514 Review.
Cited by
-
Nano selenium-enriched probiotic Lactobacillus enhances alum adjuvanticity and promotes antigen-specific systemic and mucosal immunity.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 27;14:1116223. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1116223. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36793732 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of selenoprotein extracts from Cardamine hupingshanensis on growth, selenium metabolism, antioxidant capacity, immunity and intestinal health in largemouth bass Micropterus salmoides.Front Immunol. 2024 Jan 22;15:1342210. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1342210. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38318186 Free PMC article.
-
Replacing dietary sodium selenite with biogenic selenium nanoparticles improves the growth performance and gut health of early-weaned piglets.Anim Nutr. 2023 Aug 22;15:99-113. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2023.08.003. eCollection 2023 Dec. Anim Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38023380 Free PMC article.
-
Current Understanding of Human Polymorphism in Selenoprotein Genes: A Review of Its Significance as a Risk Biomarker.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 24;25(3):1402. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031402. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338681 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of dietary selenium sources and levels on growth performance, carcass characteristics, selenium concentrations, and blood biochemistry of growing-finishing pigs.J Anim Sci Technol. 2025 May;67(3):607-618. doi: 10.5187/jast.2024.e53. Epub 2025 May 31. J Anim Sci Technol. 2025. PMID: 40519612 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Terry E.N., Michal J.J., Hostetler C.E., Kincaid R.L. Levels of mRNA for three selenoproteins in skeletal muscle of fetal and newborn pigs. Livest. Sci. 2009;124:21–25. doi: 10.1016/j.livsci.2008.12.005. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

