Irbesartan in Marfan syndrome (AIMS): a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial
- PMID: 31836196
- PMCID: PMC6934233
- DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32518-8
Irbesartan in Marfan syndrome (AIMS): a double-blind, placebo-controlled randomised trial
Abstract
Background: Irbesartan, a long acting selective angiotensin-1 receptor inhibitor, in Marfan syndrome might reduce aortic dilatation, which is associated with dissection and rupture. We aimed to determine the effects of irbesartan on the rate of aortic dilatation in children and adults with Marfan syndrome.
Methods: We did a placebo-controlled, double-blind randomised trial at 22 centres in the UK. Individuals aged 6-40 years with clinically confirmed Marfan syndrome were eligible for inclusion. Study participants were all given 75 mg open label irbesartan once daily, then randomly assigned to 150 mg of irbesartan (increased to 300 mg as tolerated) or matching placebo. Aortic diameter was measured by echocardiography at baseline and then annually. All images were analysed by a core laboratory blinded to treatment allocation. The primary endpoint was the rate of aortic root dilatation. This trial is registered with ISRCTN, number ISRCTN90011794.
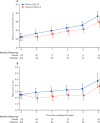
Findings: Between March 14, 2012, and May 1, 2015, 192 participants were recruited and randomly assigned to irbesartan (n=104) or placebo (n=88), and all were followed for up to 5 years. Median age at recruitment was 18 years (IQR 12-28), 99 (52%) were female, mean blood pressure was 110/65 mm Hg (SDs 16 and 12), and 108 (56%) were taking β blockers. Mean baseline aortic root diameter was 34·4 mm in the irbesartan group (SD 5·8) and placebo group (5·5). The mean rate of aortic root dilatation was 0·53 mm per year (95% CI 0·39 to 0·67) in the irbesartan group compared with 0·74 mm per year (0·60 to 0·89) in the placebo group, with a difference in means of -0·22 mm per year (-0·41 to -0·02, p=0·030). The rate of change in aortic Z score was also reduced by irbesartan (difference in means -0·10 per year, 95% CI -0·19 to -0·01, p=0·035). Irbesartan was well tolerated with no observed differences in rates of serious adverse events.
Interpretation: Irbesartan is associated with a reduction in the rate of aortic dilatation in children and young adults with Marfan syndrome and could reduce the incidence of aortic complications.
Funding: British Heart Foundation, the UK Marfan Trust, the UK Marfan Association.
Copyright © 2019 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Ltd. This is an Open Access article under the CC BY 4.0 license. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Angiotensin-II receptor blockade in Marfan syndrome.Lancet. 2019 Dec 21;394(10216):2206-2207. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)32536-X. Epub 2019 Dec 10. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31836197 No abstract available.
References
-
- Dietz HC, Cutting GR, Pyeritz RE. Marfan syndrome caused by a recurrent de novo missense mutation in the fibrillin gene. Nature. 1991;352:337–339. - PubMed
-
- Groth KA, Stochholm K, Hove H, Andersen NH, Gravholt CH. Causes of mortality in the Marfan syndrome (from a nationwide register study) Am J Cardiol. 2018;122:1231–1235. - PubMed
-
- Shores J, Berger KR, Murphy EA, Pyeritz RE. Progression of aortic dilatation and the benefit of long-term β-adrenergic blockade in Marfan's syndrome. N Engl J Med. 1994;330:1335–1341. - PubMed
-
- Ladouceur M, Fermanian C, Lupoglazoff J-M. Effect of beta-blockade on ascending aortic dilatation in children with the Marfan syndrome. Am J Cardiol. 2007;99:406–409. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

