Integrative and Network-Specific Connectivity of the Basal Ganglia and Thalamus Defined in Individuals
- PMID: 31836321
- PMCID: PMC7035165
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuron.2019.11.012
Integrative and Network-Specific Connectivity of the Basal Ganglia and Thalamus Defined in Individuals
Abstract
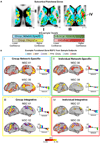
The basal ganglia, thalamus, and cerebral cortex form an interconnected network implicated in many neurological and psychiatric illnesses. A better understanding of cortico-subcortical circuits in individuals will aid in development of personalized treatments. Using precision functional mapping-individual-specific analysis of highly sampled human participants-we investigated individual-specific functional connectivity between subcortical structures and cortical functional networks. This approach revealed distinct subcortical zones of network specificity and multi-network integration. Integration zones were systematic, with convergence of cingulo-opercular control and somatomotor networks in the ventral intermediate thalamus (motor integration zones), dorsal attention and visual networks in the pulvinar, and default mode and multiple control networks in the caudate nucleus. The motor integration zones were present in every individual and correspond to consistently successful sites of deep brain stimulation (DBS; essential tremor). Individually variable subcortical zones correspond to DBS sites with less consistent treatment effects, highlighting the importance of PFM for neurosurgery, neurology, and psychiatry.
Keywords: basal ganglia; brain networks; deep brain stimulation; functional connectivity; precision functional mapping; resting state; subcortex; thalamus.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures






Comment in
-
Precision Functional Mapping of Corticostriatal and Corticothalamic Circuits: Parallel Processing Reconsidered.Neuron. 2020 Feb 19;105(4):595-597. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2020.01.025. Neuron. 2020. PMID: 32078793
References
-
- Albin RL, Young AB, and Penney JB (1989). The functional anatomy of basal ganglia disorders. Trends Neurosci 12, 366–375. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, and Crutcher MD (1990a). Basal ganglia-thalamocortical circuits: parallel substrates for motor,oculomotor,prefrontal and limbic functions. Prog Brain Res 85, 119–146. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, and Crutcher MD (1990b). Functional architecture of basal ganglia circuits: neural substrates of parallel processing. Trends Neurosci 13, 266–271. - PubMed
-
- Alexander GE, Delong MR, and Strick PL (1986). Parallel organization of functionally segregated circuits linking basal ganglia and cortex. Annu Rev Neurosci 9, 357–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

