Genome sequencing for early-onset or atypical dementia: high diagnostic yield and frequent observation of multiple contributory alleles
- PMID: 31836585
- PMCID: PMC6913143
- DOI: 10.1101/mcs.a003491
Genome sequencing for early-onset or atypical dementia: high diagnostic yield and frequent observation of multiple contributory alleles
Abstract
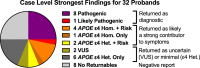
We assessed the results of genome sequencing for early-onset dementia. Participants were selected from a memory disorders clinic. Genome sequencing was performed along with C9orf72 repeat expansion testing. All returned sequencing results were Sanger-validated. Prior clinical diagnoses included Alzheimer's disease, frontotemporal dementia, and unspecified dementia. The mean age of onset was 54 (41-76). Fifty percent of patients had a strong family history, 37.5% had some, and 12.5% had no known family history. Nine of 32 patients (28%) had a variant defined as pathogenic or likely pathogenic (P/LP) by American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics standards, including variants in APP, C9orf72, CSF1R, and MAPT Nine patients (including three with P/LP variants) harbored established risk alleles with moderate penetrance (odds ratios of ∼2-5) in ABCA7, AKAP9, GBA, PLD3, SORL1, and TREM2 All six patients harboring these moderate penetrance variants but not P/LP variants also had one or two APOE ε4 alleles. One patient had two APOE ε4 alleles with no other established contributors. In total, 16 patients (50%) harbored one or more genetic variants likely to explain symptoms. We identified variants of uncertain significance (VUSs) in ABI3, ADAM10, ARSA, GRID2IP, MME, NOTCH3, PLCD1, PSEN1, TM2D3, TNK1, TTC3, and VPS13C, also often along with other variants. In summary, genome sequencing for early-onset dementia frequently identified multiple established or possible contributory alleles. These observations add support for an oligogenic model for early-onset dementia.
Keywords: Alzheimer disease; frontotemporal dementia.
© 2019 Cochran et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures

References
-
- Akimoto C, Volk AE, van Blitterswijk M, Van den Broeck M, Leblond CS, Lumbroso S, Camu W, Neitzel B, Onodera O, van Rheenen W, et al. 2014. A blinded international study on the reliability of genetic testing for GGGGCC-repeat expansions in C9orf72 reveals marked differences in results among 14 laboratories. J Med Genet 51: 419–424. 10.1136/jmedgenet-2014-102360 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bellenguez C, Charbonnier C, Grenier-Boley B, Quenez O, Le Guennec K, Nicolas G, Chauhan G, Wallon D, Rousseau S, Richard AC, et al. 2017. Contribution to Alzheimer's disease risk of rare variants in TREM2, SORL1, and ABCA7 in 1779 cases and 1273 controls. Neurobiol Aging 59: 220.e221–220.e229. 10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2017.07.001 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bis JC, Jian X, Kunkle BW, Chen Y, Hamilton-Nelson KL, Bush WS, Salerno WJ, Lancour D, Ma Y, Renton AE, et al. 2018. Whole exome sequencing study identifies novel rare and common Alzheimer's-associated variants involved in immune response and transcriptional regulation. Mol Psychiatry 10.1038/s41380-018-0112-7 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
