Proton-detected polarization optimized experiments (POE) using ultrafast magic angle spinning solid-state NMR: Multi-acquisition of membrane protein spectra
- PMID: 31837552
- PMCID: PMC7003683
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jmr.2019.106664
Proton-detected polarization optimized experiments (POE) using ultrafast magic angle spinning solid-state NMR: Multi-acquisition of membrane protein spectra
Abstract
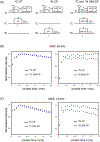
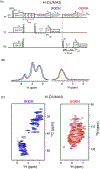
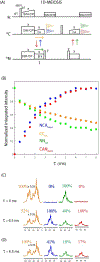
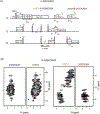
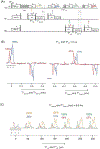
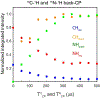
Proton-detected solid-state NMR (ssNMR) spectroscopy has dramatically improved the sensitivity and resolution of fast magic angle spinning (MAS) methods. While relatively straightforward for fibers and crystalline samples, the routine application of these techniques to membrane protein samples is still challenging. This is due to the low sensitivity of these samples, which require high lipid:protein ratios to maintain the structural and functional integrity of membrane proteins. We previously introduced a family of novel polarization optimized experiments (POE) that enable to make the best of nuclear polarization and obtain multiple-acquisitions from a single pulse sequence and one receiver. Here, we present the 1H-detected versions of POE using ultrafast MAS ssNMR. Specifically, we implemented proton detection into our three main POE strategies, H-DUMAS, H-MEIOSIS, and H-MAeSTOSO, achieving the acquisition of up to ten different experiments using a single pulse sequence. We tested these experiments on a model compound N-Acetyl-Val-Leu dipeptide and applied to a six transmembrane acetate transporter, SatP, reconstituted in lipid membranes. These new methods will speed up the spectroscopy of challenging biomacromolecules such as membrane proteins.
Keywords: H-DUMAS; H-MAeSTOSO; H-MEIOSIS; Membrane proteins; Multi-acquisition; Polarization optimized experiments (POE); SIM-CP; Solid-state NMR; Ultra-fast magic angle spinning.
Copyright © 2019 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Quinn CM; Wang M; Fritz MP; Runge B; Ahn J; Xu C; Perilla JR; Gronenborn AM; Polenova T, Dynamic regulation of HIV-1 capsid interaction with the restriction factor TRIM5alpha identified by magic-angle spinning NMR and molecular dynamics simulations. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2018, 115 (45), 11519–11524. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baldus M, GPCR: Lock and key become flexible. Nat Chem Biol 2018, 14 (3), 201–202. - PubMed
-
- Fitzpatrick AW; Debelouchina GT; Bayro MJ; Clare DK; Caporini MA; Bajaj VS; Jaroniec CP; Wang L; Ladizhansky V; Muller SA; MacPhee CE; Waudby CA; Mott HR; De Simone A; Knowles TP; Saibil HR; Vendruscolo M; Orlova EV; Griffin RG; Dobson CM, Atomic structure and hierarchical assembly of a cross-beta amyloid fibril. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 2013, 110 (14), 5468–73. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

