Dual blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with dupilumab, an IL-4Rα antibody, is required to broadly inhibit type 2 inflammation
- PMID: 31838750
- PMCID: PMC7317958
- DOI: 10.1111/all.14151
Dual blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with dupilumab, an IL-4Rα antibody, is required to broadly inhibit type 2 inflammation
Abstract
Background: Dupilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that binds IL-4Rα and inhibits signaling of both IL-4 and IL-13, has shown efficacy across multiple diseases with underlying type 2 signatures and is approved for treatment of asthma, atopic dermatitis, and chronic sinusitis with nasal polyposis. We sought to provide a comprehensive analysis of the redundant and distinct roles of IL-4 and IL-13 in type 2 inflammation and report dupilumab mechanisms of action.
Methods: Using primary cell assays and a mouse model of house dust mite-induced asthma, we compared IL-4 vs IL-13 vs IL-4Rα blockers.
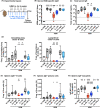
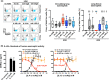
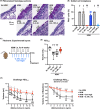
Results: Intranasal administration of either IL-4 or IL-13 confers an asthma-like phenotype in mice by inducing immune cell lung infiltration, including eosinophils, increasing cytokine/chemokine expression and mucus production, thus demonstrating redundant functions of these cytokines. We further teased out their respective contributions using human in vitro culture systems. Then, in a mouse asthma model by comparing in head-to-head studies, either IL-4 or IL-13 inhibition to dual IL-4/IL-13 inhibition, we demonstrate that blockade of both IL-4 and IL-13 is required to broadly block type 2 inflammation, which translates to protection from allergen-induced lung function impairment. Notably, only dual IL-4/IL-13 blockade prevented eosinophil infiltration into lung tissue without affecting circulating eosinophils, demonstrating that tissue, but not circulating eosinophils, contributes to disease pathology.
Conclusions: Overall, these data support IL-4 and IL-13 as key drivers of type 2 inflammation and help provide insight into the therapeutic mechanism of dupilumab, a dual IL-4/IL-13 blocker, in multiple type 2 diseases.
Keywords: IL-13; IL-4; cytokines; dupilumab; type 2 inflammation.
© 2019 The Authors. Allergy published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors are employees of Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc, and may hold stock and/or stock options in the company.
Figures




References
-
- Lambrecht BN, Hammad H, Fahy JV. The cytokines of asthma. Immunity 2019;50(4):975‐991. - PubMed
-
- May RD, Fung M. Strategies targeting the IL‐4/IL‐13 axes in disease. Cytokine 2015;75(1):89‐116. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi NA, Bennett BL, Graham NM, Pirozzi G, Stahl N, Yancopoulos GD. Targeting key proximal drivers of type 2 inflammation in disease. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 2016;15(1):35‐50. - PubMed
-
- Tan HT, Sugita K, Akdis CA. Novel biologicals for the treatment of allergic diseases and asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep 2016;16(10):70. - PubMed
-
- Gandhi NA, Pirozzi G, Graham NMH. Commonality of the IL‐4/IL‐13 pathway in atopic diseases. Exp Rev Clin Immunol 2017;13(5):425‐437. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

