Quantum expander for gravitational-wave observatories
- PMID: 31839938
- PMCID: PMC6904558
- DOI: 10.1038/s41377-019-0230-2
Quantum expander for gravitational-wave observatories
Abstract
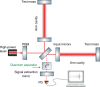
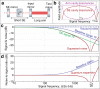
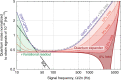
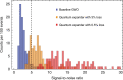
The quantum uncertainty of laser light limits the sensitivity of gravitational-wave observatories. Over the past 30 years, techniques for squeezing the quantum uncertainty, as well as for enhancing gravitational-wave signals with optical resonators have been invented. Resonators, however, have finite linewidths, and the high signal frequencies that are produced during the highly scientifically interesting ring-down of astrophysical compact-binary mergers still cannot be resolved. Here, we propose a purely optical approach for expanding the detection bandwidth. It uses quantum uncertainty squeezing inside one of the optical resonators, compensating for the finite resonators' linewidths while keeping the low-frequency sensitivity unchanged. This quantum expander is intended to enhance the sensitivity of future gravitational-wave detectors, and we suggest the use of this new tool in other cavity-enhanced metrological experiments.
Keywords: Nonlinear optics; Optical metrology; Quantum optics.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Abbott, B. P. et al. GW170817: observation of gravitational waves from a binary neutron star inspiral. Phys. Rev. Lett.119, 161101 (2017). - PubMed
-
- Abbott BP, et al. Multi-messenger observations of a binary neutron star merger. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017;848:L12. doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/aa91c9. - DOI
-
- Abbott BP, et al. Gravitational waves and gamma-rays from a binary neutron star merger: GW170817 and GRB 170817A. Astrophys. J. Lett. 2017;848:L13. doi: 10.3847/2041-8213/aa920c. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

