Pandemic influenza virus vaccines boost hemagglutinin stalk-specific antibody responses in primed adult and pediatric cohorts
- PMID: 31839997
- PMCID: PMC6898674
- DOI: 10.1038/s41541-019-0147-z
Pandemic influenza virus vaccines boost hemagglutinin stalk-specific antibody responses in primed adult and pediatric cohorts
Abstract
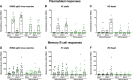
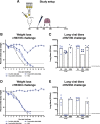
Licensed influenza virus vaccines target the head domain of the hemagglutinin (HA) glycoprotein which undergoes constant antigenic drift. The highly conserved HA stalk domain is an attractive target to increase immunologic breadth required for universal influenza virus vaccines. We tested the hypothesis that immunization with a pandemic influenza virus vaccine boosts pre-existing anti-stalk antibodies. We used chimeric cH6/1, full length H2 and H18 HA antigens in an ELISA to measure anti-stalk antibodies in recipients participating in clinical trials of A/H1N1, A/H5N1 and A/H9N2 vaccines. The vaccines induced high titers of anti-H1 stalk antibodies in adults and children, with higher titers elicited by AS03-adjuvanted vaccines. We also observed cross-reactivity to H2 and H18 HAs. The A/H9N2 vaccine elicited plasmablast and memory B-cell responses. Post-vaccination serum from vaccinees protected mice against lethal challenge with cH6/1N5 and cH5/3N4 viruses. These findings support the concept of a chimeric HA stalk-based universal influenza virus vaccine. clinicaltrials.gov: NCT02415842.
Keywords: Adjuvants; Antibodies; Immunological memory; Inactivated vaccines; Influenza virus.
© The Author(s) 2019.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interestsF.K., A.G.-S., and P.P. report study funding from the GSK group of companies. R.N., A.G.-S., P.P., F.K., C.P.M., and B.L.I. are named as inventor on a patent family regarding influenza virus vaccine constructs filed by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and the GSK group of companies. A.G.-S. also reports he is an inventor of a Mount Sinai owned patent on plasmid-based rescue technologies to generate recombinant influenza viruses with royalties paid to Medimmune. R.A.A. reports grants from National Institutes of Health, outside the submitted work. B.S., D.F., M.D., R.N.R., and C.P.M. are employed by the GSK group of companies. B.S., M.D., C.P.M., and C.C. hold shares in the GSK group of companies. C.C. and B.L.I. were employed by the GSK group of companies at the time of the study. D.S., M.A.B., A.C., W.S., and A.R. have nothing to disclose.
Figures




References
-
- World Health Organization. Influenza (seasonal). Fact sheet. http://www.who.int/en/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/influenza-(seasonal). (2019).
-
- World Health Organization. Influenza. Vaccine use. http://www.who.int/influenza/vaccines/use/en. (2019).
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

