Single-cell connectomic analysis of adult mammalian lungs
- PMID: 31840053
- PMCID: PMC6892628
- DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.aaw3851
Single-cell connectomic analysis of adult mammalian lungs
Abstract
Efforts to decipher chronic lung disease and to reconstitute functional lung tissue through regenerative medicine have been hampered by an incomplete understanding of cell-cell interactions governing tissue homeostasis. Because the structure of mammalian lungs is highly conserved at the histologic level, we hypothesized that there are evolutionarily conserved homeostatic mechanisms that keep the fine architecture of the lung in balance. We have leveraged single-cell RNA sequencing techniques to identify conserved patterns of cell-cell cross-talk in adult mammalian lungs, analyzing mouse, rat, pig, and human pulmonary tissues. Specific stereotyped functional roles for each cell type in the distal lung are observed, with alveolar type I cells having a major role in the regulation of tissue homeostasis. This paper provides a systems-level portrait of signaling between alveolar cell populations. These methods may be applicable to other organs, providing a roadmap for identifying key pathways governing pathophysiology and informing regenerative efforts.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors, some rights reserved; exclusive licensee American Association for the Advancement of Science. No claim to original U.S. Government Works. Distributed under a Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial License 4.0 (CC BY-NC).
Figures



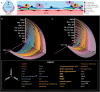
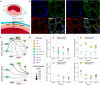

References
-
- Amit I., Winter D. R., Jung S., The role of the local environment and epigenetics in shaping macrophage identity and their effect on tissue homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 17, 18–25 (2016). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HL141852/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR001863/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG008383/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL143906/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 EB024889/EB/NIBIB NIH HHS/United States
- F30 HL143880/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 GM007205/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL138540/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL122626/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL145567/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM131642/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL145560/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 CA209992/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL127349/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

