Radial basis function for fast voltage stability assessment using Phasor Measurement Units
- PMID: 31840121
- PMCID: PMC6893073
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e02704
Radial basis function for fast voltage stability assessment using Phasor Measurement Units
Abstract
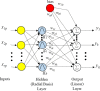
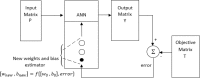
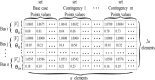
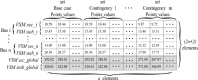
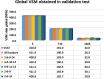
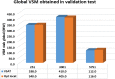
A simple method, based on Machine Learning Radial Basis Functions, RBF, is developed for estimating voltage stability margins in power systems. A reduced set of magnitude and angles of bus voltage phasors is used as input. Observability optimization technique for locating Phasor Measurement Units, PMUs, is applied. A RBF is designed and used for fast calculation of voltage stability margins for online applications with PMUs. The method allows estimating active local and global power margins in normal operation and under contingencies. Optimized placement of PMUs leads to a minimum number of these devices to estimate the margins, but is shown that it is not a matter of PMUs quantity but of PMUs location for decreasing training time or having success in estimation convergence. Compared with previous work, the most significant enhancement is that our RBF learns from PMU data. To test the proposed method, validations in the IEEE 14-bus system and in a real electrical network are done.
Keywords: Electric power transmission; Electrical engineering; Electrical system planning; Machine learning; Phasor Measurement Units; Power engineering; Power system operation; Power system planning; Power system stability; Radial basis function networks; Voltage measurement.
© 2019 The Author(s).
Figures




References
-
- Andersson G., Donalek P., Farmer R., Hatziargyriou N., Kamwa I., Kundur P., Martins N., Paserba J., Pourbeik P., Sanchez-Gasca J., Schulz R., Stankovic A., Taylor C., Vittal V. Causes of the 2003 major grid blackouts in North America and Europe, and recommended means to improve system dynamic performance. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. Oct. 2005;20(4):1922–1928.
-
- Corsi S., Sabelli C. IEEE/PES General Meeting, Denver. 2004. General blackout in Italy sunday September 28, 2003, h.03:28:00.
-
- Kurita A., Sakurai T. Proc. 27th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control, Austin. Dec. 1988. The power system failure on July 23, 1987 in Tokyo.
-
- Atputharajah A., Saha T. International Conference Industrial and Information Systems (IICIIS), Sri Lanka. Dec. 2009. Power system blackouts - literature review.
-
- Beiraghi M., Ranjbar A. Online voltage security assessment based on wide-area measurements. IEEE Trans. Power Deliv. March 2013;28(2):989–997.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

