Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy
- PMID: 31840275
- PMCID: PMC7154529
- DOI: 10.1002/mus.26782
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy
Abstract
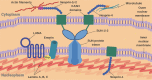
Emery-Dreifuss muscular dystrophy (EDMD) is a rare muscular dystrophy, but is particularly important to diagnose due to frequent life-threatening cardiac complications. EDMD classically presents with muscle weakness, early contractures, cardiac conduction abnormalities and cardiomyopathy, although the presence and severity of these manifestations vary by subtype and individual. Associated genes include EMD, LMNA, SYNE1, SYNE2, FHL1, TMEM43, SUN1, SUN2, and TTN, encoding emerin, lamin A/C, nesprin-1, nesprin-2, FHL1, LUMA, SUN1, SUN2, and titin, respectively. The Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man database recognizes subtypes 1 through 7, which captures most but not all of the associated genes. Genetic diagnosis is essential whenever available, but traditional diagnostic tools can help steer the evaluation toward EDMD and assist with interpretation of equivocal genetic test results. Management is primarily supportive, but it is important to monitor patients closely, especially for potential cardiac complications. There is a high potential for progress in the treatment of EDMD in the coming years.
Keywords: Emery-Dreifuss; cardiomyopathy; contractures; emerin; laminopathy; muscular dystrophy.
© 2019 The Authors. Muscle & Nerve published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
Scott A. Heller has no conflicts of interest to disclose. Peter B. Kang has served as a consultant for AveXis and ChromaDex. He has served on an advisory board for Sarepta Therapeutics. He has received honoraria from Wiley for serving as an associate editor for
Figures
References
-
- Cestan R, Lajonne NJ. Dystrophie musculaire. Iconogr Salpetriere. 1902;155:35.
-
- Becker PE, Kiener F. A new x‐chromosomal muscular dystrophy. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Z Gesamte Neurol Psychiatr. 1955;193(4):427‐448. - PubMed
-
- Rowland LP, Fetell M, Olarte M, Hays A, Singh N, Wanat FE. Emery‐Dreifuss muscular dystrophy. Ann Neurol. 1979;5(2):111‐117. - PubMed
-
- Mah JK, Korngut L, Fiest KM, et al. A systematic review and meta‐analysis on the epidemiology of the muscular dystrophies. Can J Neurol Sci. 2016;43(1):163‐177. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous