Lactate: Fueling the fire starter
- PMID: 31840439
- PMCID: PMC7187281
- DOI: 10.1002/wsbm.1474
Lactate: Fueling the fire starter
Abstract
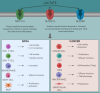
It is becoming increasingly appreciated that intermediates of metabolic pathways, besides their anabolic and catabolic functions, can act as signaling molecules and influence the outcome of immune responses. Although lactate was previously considered as a waste product of glucose metabolism, accumulating evidence has highlighted its pivotal role in regulating diverse biological processes, including immune cell polarization, differentiation and effector functions. In addition, lactate is a key player in modulating tumor immune surveillance. Hence, targeting lactate-induced signaling pathways is a promising tool to reduce inflammation, to prevent autoimmunity and to restore anti-tumor immune response. This article is characterized under: Biological Mechanisms > Metabolism.
Keywords: immunity; inflammation; lactate; metabolism; tumor.
© 2019 The Authors. WIREs Systems Biology and Medicine published by Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Abebayehu, D. , Spence, A. J. , Qayum, A. A. , Taruselli, M. T. , McLeod, J. J. , Caslin, H. L. , … Ryan, J. J. (2016). Lactic acid suppresses IL‐33‐mediated mast cell inflammatory responses via hypoxia‐inducible factor‐1alpha‐dependent miR‐155 suppression. Journal of Immunology, 197(7), 2909–2917. 10.4049/jimmunol.1600651 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

