Protein Footprinting and X-ray Crystallography Reveal the Interaction of PD-L1 and a Macrocyclic Peptide
- PMID: 31841311
- PMCID: PMC7485629
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.biochem.9b00822
Protein Footprinting and X-ray Crystallography Reveal the Interaction of PD-L1 and a Macrocyclic Peptide
Abstract
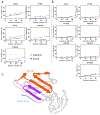
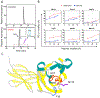
Blocking interactions between PD-1 and PD-L1 opens a new era of cancer treatment involving immunity modulation. Although most immunotherapies use monoclonal antibodies, small-molecule inhibitors offer advantages. To facilitate development of small-molecule therapeutics, we implemented a rapid approach to characterize the binding interfaces of small-molecule inhibitors with PD-L1. We determined its interaction with a synthetic macrocyclic peptide by using two mass spectrometry-based approaches, hydrogen-deuterium exchange and fast photochemical oxidation of proteins (FPOP), and corroborated the findings with our X-ray structure of the PD-L1/macrocycle complex. Although all three approaches show that the macrocycle binds directly to PD-L1 over the regions of residues 46-87 and 114-125, the two protein footprinting approaches show additional binding at the N-terminus of PD-L1, and FPOP reveals some critical binding residues. The outcomes not only show the binding regions but also demonstrate the utility of MS-based footprinting in probing protein/ligand inhibitory interactions in cancer immunotherapy.
Figures
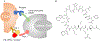


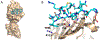
References
-
- Atkins MB; Sznol M, Cancer Immunotherapy: Past Progress and Future Directions. Semin Oncol 2015, 42 (4), 518–22. - PubMed
-
- Gubin MM; Schreiber RD, CANCER. The odds of immunotherapy success. Science 2015, 350 (6257), 158–9. - PubMed
-
- June CH; O'Connor RS; Kawalekar OU; Ghassemi S; Milone MC, CAR T cell immunotherapy for human cancer. Science 2018, 359 (6382), 1361–1365. - PubMed
-
- Page DB; Postow MA; Callahan MK; Allison JP; Wolchok JD, Immune modulation in cancer with antibodies. Annu Rev Med 2014, 65, 185–202. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

