Long-Term Results of NRG Oncology RTOG 0617: Standard- Versus High-Dose Chemoradiotherapy With or Without Cetuximab for Unresectable Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
- PMID: 31841363
- PMCID: PMC7048161
- DOI: 10.1200/JCO.19.01162
Long-Term Results of NRG Oncology RTOG 0617: Standard- Versus High-Dose Chemoradiotherapy With or Without Cetuximab for Unresectable Stage III Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer
Abstract
Purpose: RTOG 0617 compared standard-dose (SD; 60 Gy) versus high-dose (HD; 74 Gy) radiation with concurrent chemotherapy and determined the efficacy of cetuximab for stage III non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Methods: The study used a 2 × 2 factorial design with radiation dose as 1 factor and cetuximab as the other, with a primary end point of overall survival (OS).
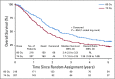
Results: Median follow-up was 5.1 years. There were 3 grade 5 adverse events (AEs) in the SD arm and 9 in the HD arm. Treatment-related grade ≥3 dysphagia and esophagitis occurred in 3.2% and 5.0% of patients in the SD arm v 12.1% and 17.4% in the HD arm, respectively (P = .0005 and < .0001). There was no difference in pulmonary toxicity, with grade ≥3 AEs in 20.6% and 19.3%. Median OS was 28.7 v 20.3 months (P = .0072) in the SD and HD arms, respectively, 5-year OS and progression-free survival (PFS) rates were 32.1% and 23% and 18.3% and 13% (P = .055), respectively. Factors associated with improved OS on multivariable analysis were standard radiation dose, tumor location, institution accrual volume, esophagitis/dysphagia, planning target volume and heart V5. The use of cetuximab conferred no survival benefit at the expense of increased toxicity. The prior signal of benefit in patients with higher H scores was no longer apparent. The progression rate within 1 month of treatment completion in the SD arm was 4.6%. For comparison purposes, the resultant 2-year OS and PFS rates allowing for that dropout rate were 59.6% and 30.7%, respectively, in the SD arms.
Conclusion: A 60-Gy radiation dose with concurrent chemotherapy should remain the standard of care, with the OS rate being among the highest reported in the literature for stage III NSCLC. Cetuximab had no effect on OS. The 2-year OS rates in the control arm are similar to the PACIFIC trial.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT00533949.
Figures

References
-
- Bradley JD, Paulus R, Komaki R, et al. Standard-dose versus high-dose conformal radiotherapy with concurrent and consolidation carboplatin plus paclitaxel with or without cetuximab for patients with stage IIIA or IIIB non-small-cell lung cancer (RTOG 0617): A randomised, two-by-two factorial phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:187–199. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonia SJ, Villegas A, Daniel D, et al. Overall survival with durvalumab after chemoradiotherapy in stage III NSCLC. N Engl J Med. 2018;379:2342–2350. - PubMed
-
- Haybittle JL. Repeated assessment of results in clinical trials of cancer treatment. Br J Radiol. 1971;44:793–797. - PubMed
-
- Freidlin B, Korn EL. A comment on futility monitoring. Control Clin Trials. 2002;23:355–366. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

