Evaluating the reliability of neurocognitive biomarkers of neurodegenerative diseases across countries: A machine learning approach
- PMID: 31841681
- PMCID: PMC7008715
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116456
Evaluating the reliability of neurocognitive biomarkers of neurodegenerative diseases across countries: A machine learning approach
Abstract
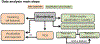
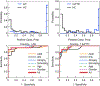
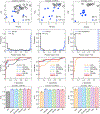
Accurate early diagnosis of neurodegenerative diseases represents a growing challenge for current clinical practice. Promisingly, current tools can be complemented by computational decision-support methods to objectively analyze multidimensional measures and increase diagnostic confidence. Yet, widespread application of these tools cannot be recommended unless they are proven to perform consistently and reproducibly across samples from different countries. We implemented machine-learning algorithms to evaluate the prediction power of neurocognitive biomarkers (behavioral and imaging measures) for classifying two neurodegenerative conditions -Alzheimer Disease (AD) and behavioral variant frontotemporal dementia (bvFTD)- across three different countries (>200 participants). We use machine-learning tools integrating multimodal measures such as cognitive scores (executive functions and cognitive screening) and brain atrophy volume (voxel based morphometry from fronto-temporo-insular regions in bvFTD, and temporo-parietal regions in AD) to identify the most relevant features in predicting the incidence of the diseases. In the Country-1 cohort, predictions of AD and bvFTD became maximally improved upon inclusion of cognitive screenings outcomes combined with atrophy levels. Multimodal training data from this cohort allowed predicting both AD and bvFTD in the other two novel datasets from other countries with high accuracy (>90%), demonstrating the robustness of the approach as well as the differential specificity and reliability of behavioral and neural markers for each condition. In sum, this is the first study, across centers and countries, to validate the predictive power of cognitive signatures combined with atrophy levels for contrastive neurodegenerative conditions, validating a benchmark for future assessments of reliability and reproducibility.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Classification; Executive functions; Frontotemporal dementia; Machine-learning; Voxel-based morphometry.
Copyright © 2019 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declarations of competing interest None.
Figures
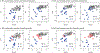
References
-
- Amieva H, Lafont S, Rouch-Leroyer I, et al., 2004. Evidencing inhibitory deficits in Alzheimer’s disease through interference effects and shifting disabilities in the Stroop test. Arch. Clin. Neuropsychol. : Off. J. Natl. Acad. Neuropsychologists 19 (6), 791–803. - PubMed
-
- Baez S, Couto B, Torralva T, et al., 2014. Comparing moral judgments of patients with frontotemporal dementia and frontal stroke. JAMA neurology 71 (9), 1172–1176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

