Identification of TRIM25 as a Negative Regulator of Caspase-2 Expression Reveals a Novel Target for Sensitizing Colon Carcinoma Cells to Intrinsic Apoptosis
- PMID: 31842382
- PMCID: PMC6952940
- DOI: 10.3390/cells8121622
Identification of TRIM25 as a Negative Regulator of Caspase-2 Expression Reveals a Novel Target for Sensitizing Colon Carcinoma Cells to Intrinsic Apoptosis
Abstract
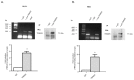
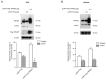
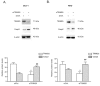
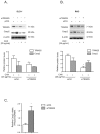
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is one of the most common cancers that is characterized by a high mortality due to the strong metastatic potential of the primary tumor and the high rate of therapy resistance. Hereby, evasion of apoptosis is the primary underlying cause of reduced sensitivity of tumor cells to chemo- and radiotherapy. Using RNA affinity chromatography, we identified the tripartite motif-containing protein 25 (TRIM25) as a bona fide caspase-2 mRNA-binding protein in colon carcinoma cells. Loss-of-function and gain-of-function approaches revealed that TRIM25 attenuates the protein levels of caspase-2 without significantly affecting caspase-2 mRNA levels. In addition, experiments with cycloheximide revealed that TRIM25 does not affect the protein stability of caspase-2. Furthermore, silencing of TRIM25 induced a significant redistribution of caspase-2 transcripts from RNP particles to translational active polysomes, indicating that TRIM25 negatively interferes with caspase-2 translation. Functionally, the elevation in caspase-2 upon TRIM25 depletion significantly increased the sensitivity of colorectal cells to drug-induced intrinsic apoptosis as implicated by increased caspase-3 cleavage and cytochrome c release. Importantly, the apoptosis-sensitizing effects by transient TRIM25 knockdown were rescued by concomitant silencing of caspase-2, demonstrating a critical role of caspase-2. Inhibition of caspase-2 by TRIM25 implies a survival mechanism that critically contributes to chemotherapeutic drug resistance in CRC.
Keywords: TRIM25; caspase-2; chemotherapy resistance; colon carcinoma cells; intrinsic apoptosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The E3 Ligase TRIM25 Impairs Apoptotic Cell Death in Colon Carcinoma Cells via Destabilization of Caspase-7 mRNA: A Possible Role of hnRNPH1.Cells. 2023 Jan 3;12(1):201. doi: 10.3390/cells12010201. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36611995 Free PMC article.
-
TRIM25: A Global Player of Cell Death Pathways and Promising Target of Tumor-Sensitizing Therapies.Cells. 2025 Jan 7;14(2):65. doi: 10.3390/cells14020065. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851496 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The ubiquitin ligase TRIM25 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma progression by targeting metastasis associated 1 protein.IUBMB Life. 2017 Oct;69(10):795-801. doi: 10.1002/iub.1661. Epub 2017 Aug 31. IUBMB Life. 2017. PMID: 28861931
-
Attenuation of the ELAV1-like protein HuR sensitizes adenocarcinoma cells to the intrinsic apoptotic pathway by increasing the translation of caspase-2L.Cell Death Dis. 2014 Jul 10;5(7):e1321. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2014.279. Cell Death Dis. 2014. PMID: 25010987 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibition of Caspase-2 Translation by the mRNA Binding Protein HuR: A Novel Path of Therapy Resistance in Colon Carcinoma Cells?Cells. 2019 Jul 30;8(8):797. doi: 10.3390/cells8080797. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31366165 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The E3 Ligase TRIM25 Impairs Apoptotic Cell Death in Colon Carcinoma Cells via Destabilization of Caspase-7 mRNA: A Possible Role of hnRNPH1.Cells. 2023 Jan 3;12(1):201. doi: 10.3390/cells12010201. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36611995 Free PMC article.
-
Identification and Validation of TRIM25 as a Glucose Metabolism Regulator in Prostate Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 19;23(16):9325. doi: 10.3390/ijms23169325. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36012594 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular communication network 1 promotes CASP2 mRNA expression but suppresses its protein translation in esophageal adenocarcinoma.J Cell Commun Signal. 2024 Jul 17;18(3):e12046. doi: 10.1002/ccs3.12046. eCollection 2024 Sep. J Cell Commun Signal. 2024. PMID: 39524140 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Mechanisms, Biomarkers, and Therapeutic Targets of TRIM Family in Gastrointestinal Cancer.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024 Dec 5;18:5615-5639. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S482340. eCollection 2024. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2024. PMID: 39654601 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIM25: A Global Player of Cell Death Pathways and Promising Target of Tumor-Sensitizing Therapies.Cells. 2025 Jan 7;14(2):65. doi: 10.3390/cells14020065. Cells. 2025. PMID: 39851496 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Flanagan L., Kehoe J., Fay J., Bacon O., Lindner A.U., Kay E.W., Deasy J., McNamara D.A., Prehn J.H. High levels of X-linked Inhibitor-of-Apoptosis Protein (XIAP) are indicative of radio chemotherapy resistance in rectal cancer. Radiat. Oncol. 2015;10:131. doi: 10.1186/s13014-015-0437-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sprenger T., Rodel F., Beissbarth T., Conradi L.C., Rothe H., Homayounfar K., Wolff H.A., Ghadimi B.M., Yildirim M., Becker H., et al. Failure of downregulation of survivin following neoadjuvant radiochemotherapy in rectal cancer is associated with distant metastases and shortened survival. Clin Cancer Res. 2011;17:1623–1631. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2592. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

