Effect of Nano-SiOx/Chitosan Complex Coating on the Physicochemical Characteristics and Preservation Performance of Green Tomato
- PMID: 31842429
- PMCID: PMC6943560
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24244552
Effect of Nano-SiOx/Chitosan Complex Coating on the Physicochemical Characteristics and Preservation Performance of Green Tomato
Abstract
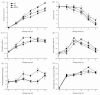
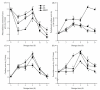
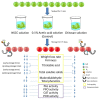
A novel nano-silicon oxides (SiOx)/chitosan complex film was prepared using ultrasonic assistant in the process of dissolving chitosan and silicon oxides (SiOx), and characterized by transmission electron microscopy. Its effect on quality preservation of tomatoes (Solanum lycopersicum L. cv. Zheza 205) was investigated under ambient temperature. The results revealed that the nano-SiOx/chitosan complex (NSCC) film retarded weight loss and softness, delayed the titratable acids and total soluble solids loss, and thus markedly extended shelf life of green tomatoes. The antimicrobial activity of tomatoes coated with NSCC film was also recorded higher compared to chitosan (Ch) films and control. In addition, the NSCC film-coated tomatoes prevent the increase of malondialdehyde content and total polyphenol content. Moreover, the peroxidase activity, phenylalanine ammonia-lyase activity, and polyphenoloxidase activity of tomatoes coated with NSCC film were found lower than that in other treatments. These data indicated that the beneficial effects of nano-SiOx/chitosan complex coating on postharvest quality were possibly associated with the lower rate of O2/CO2 transmission coefficient, limiting food-borne pathogenic bacterial growth, higher antioxidant activities, and also higher reactive oxygen species (ROS) scavenging and anti-browning activities of related enzymes in the tomatoes. Further, the results of the study could be used to successfully develop a novel nano-SiOx/chitosan complex film for improving the postharvested quality of tomatoes and thus effectively utilized by the food packaging industry.
Keywords: enzyme activities; green tomato; microbial load; nano-SiOx/chitosan complex coating; postharvest quality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Chaturvedi K., Sharma N., Yadav S.K. Composite edible coatings from commercial pectin, corn flour and beetroot powder minimize post-harvest decay, reduces ripening and improves sensory liking of tomatoes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019;133:284–293. - PubMed
-
- Cuvi M.J.A., Vicente A.R., Concellón A., Chaves A.R. Changes in red pepper antioxidants as affected by UV-C treatments and storage at chilling temperatures. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2011;44:1666–1671. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2011.01.027. - DOI
-
- Shewfelt R.L., Erickson M.C. Role of lipid peroxidation in the mechanism of membrane-associated disorders in edible plant tissue. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 1991;2:152–154. doi: 10.1016/0924-2244(91)90661-2. - DOI
-
- Balasundram N., Sundram K., Samman S. Phenolic compounds in plants and agri-industrial by-products: Antioxidant activity, occurrence, and potential uses. Food Chem. 2006;99:191–203. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2005.07.042. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

