Splenic cord capillary hemangioma with non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia: a case report
- PMID: 31842913
- PMCID: PMC6915897
- DOI: 10.1186/s13000-019-0915-0
Splenic cord capillary hemangioma with non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia: a case report
Abstract
Background: Splenic cord capillary hemangioma is a rare benign vascular lesion classified as a splenic hamartoma. On the other hand, non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia (NICTH) is one of the rare causes of spontaneous hypoglycemia and is considered to be one of the paraneoplastic syndromes. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first reported case of a splenic cord capillary hemangioma with NICTH.
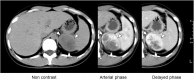
Case presentation: A 25-year-old male was referred to our hospital with hypoglycemia. Except for his low blood sugar, there were no abnormal findings from laboratory tests, which included an endocrinological examination. Enhanced computed tomography confirmed the presence of a solid mass measuring about 6 cm in the retroperitoneum, and a tumorectomy was performed. During this operation, it became clear that the tumor turned out to be a splenic parenchyma, and as a result, a total splenectomy was performed. Microscopically, we diagnosed this as a cord capillary hemangioma, and through immunohistochemistry, we found that some tumor cells were positive for insulin-like growth factor -II. Fortunately, the hypoglycemia-related symptoms disappeared after surgical resection was performed. The patient is still alive and well without evidence of local tumor recurrence 15 years after the operation.
Conclusions: Splenic cord capillary hemangioma, one of the types of splenic hamartomas, is a very rare benign vascular lesion and might be associated with hypoglycemia thought to be NICTH.
Keywords: Insulin-like growth factor-II; Non-islet cell tumor hypoglycemia; Splenic cord capillary hemangioma; Splenic hamartoma; Splenic tumor.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

