Benchmarking transposable element annotation methods for creation of a streamlined, comprehensive pipeline
- PMID: 31843001
- PMCID: PMC6913007
- DOI: 10.1186/s13059-019-1905-y
Benchmarking transposable element annotation methods for creation of a streamlined, comprehensive pipeline
Abstract
Background: Sequencing technology and assembly algorithms have matured to the point that high-quality de novo assembly is possible for large, repetitive genomes. Current assemblies traverse transposable elements (TEs) and provide an opportunity for comprehensive annotation of TEs. Numerous methods exist for annotation of each class of TEs, but their relative performances have not been systematically compared. Moreover, a comprehensive pipeline is needed to produce a non-redundant library of TEs for species lacking this resource to generate whole-genome TE annotations.
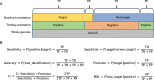
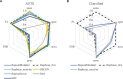
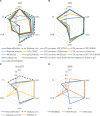
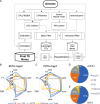
Results: We benchmark existing programs based on a carefully curated library of rice TEs. We evaluate the performance of methods annotating long terminal repeat (LTR) retrotransposons, terminal inverted repeat (TIR) transposons, short TIR transposons known as miniature inverted transposable elements (MITEs), and Helitrons. Performance metrics include sensitivity, specificity, accuracy, precision, FDR, and F1. Using the most robust programs, we create a comprehensive pipeline called Extensive de-novo TE Annotator (EDTA) that produces a filtered non-redundant TE library for annotation of structurally intact and fragmented elements. EDTA also deconvolutes nested TE insertions frequently found in highly repetitive genomic regions. Using other model species with curated TE libraries (maize and Drosophila), EDTA is shown to be robust across both plant and animal species.
Conclusions: The benchmarking results and pipeline developed here will greatly facilitate TE annotation in eukaryotic genomes. These annotations will promote a much more in-depth understanding of the diversity and evolution of TEs at both intra- and inter-species levels. EDTA is open-source and freely available: https://github.com/oushujun/EDTA.
Keywords: Annotation; Benchmarking; Genome; Pipeline; Transposable element.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Comment in
-
Accounting for diverse transposable element landscapes is key to developing and evaluating accurate de novo annotation strategies.Genome Biol. 2024 Jan 2;25(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s13059-023-03118-1. Genome Biol. 2024. PMID: 38166955 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McClintock B. Cytogenetic studies of maize and Neurospora. Year B Carnegie Inst Wash. 1947;46:146–152.
-
- International Wheat Genome Sequencing Consortium (IWGSC), IWGSC RefSeq principal investigators. Appels R, Eversole K, Feuillet C, Keller B, et al. Shifting the limits in wheat research and breeding using a fully annotated reference genome. Science. 2018;361:eaar7191. doi: 10.1126/science.aar7191. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

