PSPC1-interchanged interactions with PTK6 and β-catenin synergize oncogenic subcellular translocations and tumor progression
- PMID: 31844057
- PMCID: PMC6914800
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13665-6
PSPC1-interchanged interactions with PTK6 and β-catenin synergize oncogenic subcellular translocations and tumor progression
Abstract
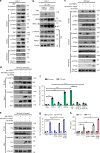
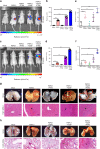
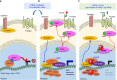
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is one of the most lethal cancers worldwide due to metastasis. Paraspeckle component 1 (PSPC1) upregulation has been identified as an HCC pro-metastatic activator associated with poor patient prognosis, but with a lack of targeting strategy. Here, we report that PSPC1, a nuclear substrate of PTK6, sequesters PTK6 in the nucleus and loses its metastasis driving capability. Conversely, PSPC1 upregulation or PSPC1-Y523F mutation promotes epithelial-mesenchymal transition, stemness, and metastasis via cytoplasmic translocation of active PTK6 and nuclear translocation of β-catenin, which interacts with PSPC1 to augment Wnt3a autocrine signaling. The aberrant nucleocytoplasmic shuttling of active PTK6/β-catenin is reversed by expressing the PSPC1 C-terminal interacting domain (PSPC1-CT131), thereby suppressing PSPC1/PTK6/β-catenin-activated metastasis to prolong the survival of HCC orthotopic mice. Thus, PSPC1 is the contextual determinant of the oncogenic switch of PTK6/β-catenin subcellular localizations, and PSPC1-CT131 functions as a dual inhibitor of PSPC1 and PTK6 with potential for improving cancer therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





Similar articles
-
PSPC1 is a new contextual determinant of aberrant subcellular translocation of oncogenes in tumor progression.J Biomed Sci. 2021 Aug 2;28(1):57. doi: 10.1186/s12929-021-00753-3. J Biomed Sci. 2021. PMID: 34340703 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PSPC1: a contextual determinant of tumor progression.Mol Cell Oncol. 2020 Feb 3;7(2):1721253. doi: 10.1080/23723556.2020.1721253. eCollection 2020. Mol Cell Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32158931 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Nuclear Paraspeckles: Induction in Chemoresistance and Prediction for Poor Survival.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019;52(4):787-801. doi: 10.33594/000000055. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2019. PMID: 30946555
-
PSPC1 mediates TGF-β1 autocrine signalling and Smad2/3 target switching to promote EMT, stemness and metastasis.Nat Cell Biol. 2018 Apr;20(4):479-491. doi: 10.1038/s41556-018-0062-y. Epub 2018 Mar 28. Nat Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29593326
-
Context-specific protein tyrosine kinase 6 (PTK6) signalling in prostate cancer.Eur J Clin Invest. 2013 Apr;43(4):397-404. doi: 10.1111/eci.12050. Epub 2013 Feb 10. Eur J Clin Invest. 2013. PMID: 23398121 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PSPC1 is a potential prognostic marker for hormone-dependent breast cancer patients and modulates RNA processing of ESR1 and SCFD2.Sci Rep. 2022 Jun 9;12(1):9495. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-13601-7. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35681031 Free PMC article.
-
LncRNA LOC105369504 inhibits tumor proliferation and metastasis in colorectal cancer by regulating PSPC1.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Mar 10;9(1):89. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01384-3. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 36894530 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological targeting PTK6 inhibits the JAK2/STAT3 sustained stemness and reverses chemoresistance of colorectal cancer.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021 Sep 22;40(1):297. doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02059-6. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34551797 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear receptor 4A1 (NR4A1) antagonists target paraspeckle component 1 (PSPC1) in cancer cells.Mol Carcinog. 2022 Jan;61(1):73-84. doi: 10.1002/mc.23362. Epub 2021 Oct 26. Mol Carcinog. 2022. PMID: 34699643 Free PMC article.
-
DDIAS, DNA damage-induced apoptosis suppressor, is a potential therapeutic target in cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2023 May;55(5):879-885. doi: 10.1038/s12276-023-00974-6. Epub 2023 May 1. Exp Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37121974 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

