Soluble fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 1 Localization in Renal Biopsies of CKD
- PMID: 31844810
- PMCID: PMC6895657
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ekir.2019.08.004
Soluble fms-Like Tyrosine Kinase 1 Localization in Renal Biopsies of CKD
Abstract
Introduction: Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 (sFLT1) is a splice variant of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) receptor lacking the transmembrane and cytoplasmic domains and acts as a powerful antagonist of VEGF signaling. Plasma sFLT1 levels are higher in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) and correlate with renal dysfunction. The source of plasma sFLT1 in CKD is unclear.
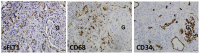
Methods: Fifty-two renal biopsies were studied for sFLT1 expression using immunohistochemistry and evaluated on a 0-4 grading scale of positive cells within inflammatory infiltrates. These included drug-induced interstitial nephritis (6); allografts (12), with polyomavirus nephritis (3); diabetes mellitus (10); lupus glomerulonephritis (6); pauci-immune vasculitis (7); IgA nephropathy (6); and miscellaneous CKD (5).
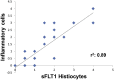
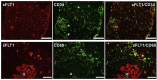
Results: Forty-seven biopsies had inflammatory infiltrates of which 37 had sFLT1-positive cells: of these biopsies, 3 were grade 4, i.e., had cells that constituted more than 50% of the inflammatory infiltrate, 9 were grade 3 (25%-50%), 5 were grade 2 (10%-25%), 3 were grade 1 (10%), and 17 were grade 0.5 (<10%). There was a robust correlation (r2 = 0.89) between degree of inflammation and sFLT1-positive cells. CD68/sFLT1 co-immunostaining studies indicated that sFLT1-positive cells were histiocytes. The surrounding capillary network was reduced.
Conclusion: sFLT1-positive histiocytes are generally part of the inflammatory infiltrates noted in CKD and are particularly abundant in forms of interstitial nephritis. Their presence promotes an anti-angiogenic state locally in the tubulointerstitium that could inhibit capillary repair, contribute to peritubular capillary loss, and enhance fibrosis in CKD.
Keywords: CKD; histiocytes/macrophages; sFLT1.
© 2019 International Society of Nephrology. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures

Similar articles
-
The VEGF decoy receptor soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 binds to macrophages.Angiogenesis. 2025 May 2;28(3):28. doi: 10.1007/s10456-025-09980-w. Angiogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40314836 Free PMC article.
-
The VEGF Inhibitor Soluble Fms-like Tyrosine Kinase 1 Does Not Promote AKI-to-CKD Transition.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 26;23(17):9660. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179660. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077058 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase-1 and soluble endoglin in HIV-associated preeclampsia.Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013 Sep;170(1):100-5. doi: 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2013.05.021. Epub 2013 Jun 24. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2013. PMID: 23806447
-
Soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 and soluble endoglin are elevated circulating anti-angiogenic factors in pre-eclampsia.Pregnancy Hypertens. 2012 Oct;2(4):358-67. doi: 10.1016/j.preghy.2012.06.003. Epub 2012 Jul 6. Pregnancy Hypertens. 2012. PMID: 26105603 Review.
-
Cytokines, angiogenic, and antiangiogenic factors and bioactive lipids in preeclampsia.Nutrition. 2015 Sep;31(9):1083-95. doi: 10.1016/j.nut.2015.03.013. Epub 2015 Apr 29. Nutrition. 2015. PMID: 26233865 Review.
Cited by
-
Peritubular Capillary Rarefaction: An Underappreciated Regulator of CKD Progression.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Nov 4;21(21):8255. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218255. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33158122 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Expression and Molecular Mechanisms of Matrix Metalloproteinase- 9 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor in Renal Interstitial Fibrosis in Rats.Curr Mol Med. 2024;24(12):1540-1549. doi: 10.2174/0115665240264823231101103226. Curr Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 37936436
-
The VEGF decoy receptor soluble Fms-like tyrosine kinase 1 binds to macrophages.Angiogenesis. 2025 May 2;28(3):28. doi: 10.1007/s10456-025-09980-w. Angiogenesis. 2025. PMID: 40314836 Free PMC article.
-
The soluble VEGF receptor sFlt-1 contributes to endothelial dysfunction in IgA nephropathy.PLoS One. 2020 Aug 13;15(8):e0234492. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0234492. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 32790760 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Levine R.J., Maynard S.E., Qian C. Circulating angiogenic factors and the risk of preeclampsia. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:672–683. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

