Lipoprotein Drug Delivery Vehicles for Cancer: Rationale and Reason
- PMID: 31847457
- PMCID: PMC6940806
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms20246327
Lipoprotein Drug Delivery Vehicles for Cancer: Rationale and Reason
Abstract
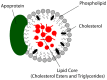
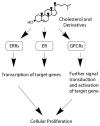
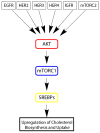
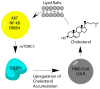
Lipoproteins are a family of naturally occurring macromolecular complexes consisting amphiphilic apoproteins, phospholipids, and neutral lipids. The physiological role of mammalian plasma lipoproteins is to transport their apolar cargo (primarily cholesterol and triglyceride) to their respective destinations through a highly organized ligand-receptor recognition system. Current day synthetic nanoparticle delivery systems attempt to accomplish this task; however, many only manage to achieve limited results. In recent years, many research labs have employed the use of lipoprotein or lipoprotein-like carriers to transport imaging agents or drugs to tumors. The purpose of this review is to highlight the pharmacologic, clinical, and molecular evidence for utilizing lipoprotein-based formulations and discuss their scientific rationale. To accomplish this task, evidence of dynamic drug interactions with circulating plasma lipoproteins are presented. This is followed by epidemiologic and molecular data describing the association between cholesterol and cancer.
Keywords: cancer imaging; cancer therapy; cholesterol; lipoprotein; nanoparticle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest with the contents of this article. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Figures

References
-
- Patra J.K., Das G., Fraceto L.F., Campos E.V.R., Rodriguez-Torres M.d.P., Acosta-Torres L.S., Diaz-Torres L.A., Grillo R., Swamy M.K., Sharma S., et al. Nano based drug delivery systems: Recent developments and future prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018;16:71. doi: 10.1186/s12951-018-0392-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

