Characterization and Identification of Prenylated Flavonoids from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. Roots by Quadrupole Time-Of-Flight and Linear Trap Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry
- PMID: 31847475
- PMCID: PMC6943520
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules24244591
Characterization and Identification of Prenylated Flavonoids from Artocarpus heterophyllus Lam. Roots by Quadrupole Time-Of-Flight and Linear Trap Quadrupole Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry
Abstract
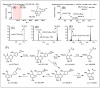
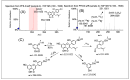
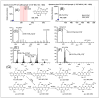
In this study, a combination of quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (Q-TOF-MS) and linear trap quadrupole orbitrap mass spectrometry (LTQ-Orbitrap-MS) was performed to investigate the fragmentation behaviors of prenylated flavonoids (PFs) from Artocarpus plants. Fifteen PFs were selected as the model molecules and divided into five types (groups A-E) according to their structural characteristics in terms of the position and existing form of prenyl substitution in the flavone skeleton. The LTQ-Orbitrap-MSn spectra of the [M - H]- ions for these compounds provided a wealth of structural information on the five different types of compounds. The main fragmentation pathways of group A were the ortho effect and retro Diels-Alder (RDA), and common losses of C4H10, CO, and CO2. The compounds in group B easily lose C6H12, forming a stable structure of a 1,4-dienyl group, unlike those in group A. The fragmentation pathway for group C is characterized by obvious 1,4A-, 1,4B- cracking of the C ring. The diagnostic fragmentation for group D is obvious RDA cracking of the C ring and the successive loss of CH3 and H2O in the LTQ-Orbitrap-MSn spectra. Fragmentation with successive loss of CO or CO2, ·CH3, and CH4 in the LTQ-Orbitrap-MSn spectra formed the characteristics of group E. The summarized fragmentation rules were successfully exploited to identify PFs from Artocarpus heterophyllus, a well-known Artocarpus plant, which led to the identification of a total of 47 PFs in this plant.
Keywords: Artocarpus heterophyllus; LTQ-Orbitrap-MS; Q-TOF-MS; fragmentation rules; identification; prenylated flavonoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures





References
-
- Bourjot M., Apel C., Martin M.T., Grellier P., Nguyen V.H., Gueritte F., Litaudon M. Antiplasmodial, antitrypanosomal, and cytotoxic activities of prenylated flavonoids isolated from the stem bark of Artocarpus styracifolius. Planta Med. 2010;76:1600–1604. doi: 10.1055/s-0030-1249777. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

