Sensitivity of the global carbonate weathering carbon-sink flux to climate and land-use changes
- PMID: 31848344
- PMCID: PMC6917807
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-019-13772-4
Sensitivity of the global carbonate weathering carbon-sink flux to climate and land-use changes
Abstract
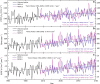
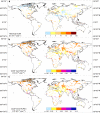
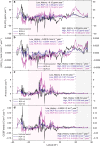
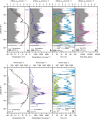
The response of carbonate weathering carbon-sink flux (CCSF) to its environmental drivers is still not well understood on the global scale. This hinders understanding of the terrestrial carbon cycle. Here, we show that there is likely to be a widespread and consistent increase in the global CCSF (ranging from + 9.8% (RCP4.5) to + 17.1% (RCP8.5)) over the period 1950-2100. In the coming years the increasing temperature might be expected to have a negative impact on carbonate weathering. However, the increasing rainfall and anticipated land-use changes will counteract this, leading to a greater CCSF. This finding has been obtained by using long-term historical (1950-2005) and modeled future (2006-2100) data for two scenarios (RCP4.5 and RCP8.5) for climate and land-use change in our CCSF equilibrium model. This study stresses the potential role that carbonate weathering may play in the evolution of the global carbon cycle over this century.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Arora VK, Boer GJ. Uncertainties in the 20th century carbon budget associate with land use change. Glob. Change Biol. 2010;16:3327–3348. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2486.2010.02202.x. - DOI
-
- Gislason SR, et al. Direct evidence of the feedback between climate and weathering. Earth Planet. Sci. Lett. 2009;277:213–2222. doi: 10.1016/j.epsl.2008.10.018. - DOI
-
- Liu Z, Dreybrodt W, Wang H. A new direction in effective accounting for the atmospheric CO2 budget: Considering the combined action of carbonate dissolution, the global water cycle and photosynthetic uptake of DIC by aquatic organisms. Earth-Sci. Rev. 2010;99:162–172. doi: 10.1016/j.earscirev.2010.03.001. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

