Conformational exchange in the potassium channel blocker ShK
- PMID: 31848433
- PMCID: PMC6917819
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-55806-3
Conformational exchange in the potassium channel blocker ShK
Abstract
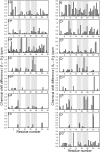
ShK is a 35-residue disulfide-linked polypeptide produced by the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus, which blocks the potassium channels Kv1.1 and Kv1.3 with pM affinity. An analogue of ShK has been developed that blocks Kv1.3 > 100 times more potently than Kv1.1, and has completed Phase 1b clinical trials for the treatment of autoimmune diseases such as psoriasis and rheumatoid arthritis. Previous studies have indicated that ShK undergoes a conformational exchange that is critical to its function, but this has proved difficult to characterise. Here, we have used high hydrostatic pressure as a tool to increase the population of the alternative state, which is likely to resemble the active form that binds to the Kv1.3 channel. By following changes in chemical shift with pressure, we have derived the chemical shift values of the low- and high-pressure states, and thus characterised the locations of structural changes. The main difference is in the conformation of the Cys17-Cys32 disulfide, which is likely to affect the positions of the critical Lys22-Tyr23 pair by twisting the 21-24 helix and increasing the solvent exposure of the Lys22 sidechain, as indicated by molecular dynamics simulations.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Pohl J, et al. Assignment of the three disulfide bonds in ShK toxin: A potent potassium channel inhibitor from the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus. Letts Peptide Sci. 1995;1:291–297. doi: 10.1007/bf00119770. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

