Metabolic Control of Epigenetics and Its Role in CD8+ T Cell Differentiation and Function
- PMID: 31849941
- PMCID: PMC6901948
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.02718
Metabolic Control of Epigenetics and Its Role in CD8+ T Cell Differentiation and Function
Abstract
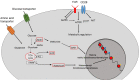
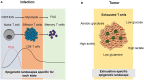
Epigenetic programs that control posttranslational modifications of histone proteins and DNA itself tightly regulate transcriptional networks determining the identity and function of CD8+ T cells. Chromatin-modifying enzymes such as histone acetyltransferases and deacetylases, represent key molecular determinants of the epigenetic imprinting of CD8+ T cells. The functions of these enzymes highly depend on the availability of key products of cellular metabolism pathways such as acetyl-CoA, NAD (Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) and SEM (S-adenosylmethionine), suggesting that there is a close crosstalk between the metabolic and the epigenetic regulation of CD8+ T cells. In this review, we will discuss the metabolic regulation of CD8+ T cell epigenetics during activation and differentiation. We will furthermore summarize how metabolic signals from the tumor microenvironment (TME) shape the epigenetic landscape of CD8+ T cells to better understand the mechanism underlying CD8+ T cell exhaustion in anti-tumor and anti-viral immunity, which might help to overcome limitations of current CD8+ T cell-based therapies.
Keywords: CD8 T cell; anti-tumor immunity; anti-viral immunity; epigenetics; exhaustion; metabolism.
Copyright © 2019 Yerinde, Siegmund, Glauben and Weidinger.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

