Impact of corneal parameters on intraocular pressure measurements in different tonometry methods
- PMID: 31850168
- PMCID: PMC6901878
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2019.12.06
Impact of corneal parameters on intraocular pressure measurements in different tonometry methods
Abstract
Aim: To evaluate the impact of central corneal thickness (CCT) and corneal curvature on intraocular pressure (IOP) measurements performed by three different tonometers.
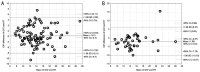
Methods: IOP in 132 healthy eyes of 66 participants was measured using three different tonometry techniques: Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT), Pascal dynamic contour tonometer (DCT), and ICare rebound tonometer (RT). CCT and corneal curvature were assessed.
Results: In healthy eyes, DCT presents significantly higher values of IOP than GAT (17.34±3.69 and 15.27±4.06 mm Hg, P<0.0001). RT measurements are significantly lower than GAT (13.56±4.33 mm Hg, P<0.0001). Compared with GAT, DCT presented on average 2.51 mm Hg higher values in eyes with CCT<600 µm and 0.99 mm Hg higher results in eyes with CCT≥600 µm. The RT results were lower on average by 1.61 and 1.95 mm Hg than those obtained by GAT, respectively. Positive correlations between CCT in eyes with CCT<600 µm were detected for all IOP measurement techniques, whereas a similar relationship was not observed in eyes with thicker corneas. A correlation between IOP values and keratometry in the group with CCT<600 µm was not detected with any of the tonometry methods. In thicker corneas, a positive correlation was found for GAT and mean keratometry values (R=0.369, P=0.005).
Conclusion: The same method should always be chosen for routine IOP control, and measurements obtained by different methods cannot be compared. All analysed tonometry methods are dependent on CCT; thus, CCT should be taken into consideration for both diagnostics and monitoring.
Keywords: Goldmann applanation tonometer; ICare rebound tonometer; Pascal dynamic contour tonometer; central corneal thickness; corneal curvature; healthy individuals; intraocular pressure.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

References
-
- ElMallah MK, Asrani SG. New ways to measure intraocular pressure. Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2008;19(2):122–126. - PubMed
-
- Medeiros FA, Weinreb RN. Evaluation of the influence of corneal biomechanical properties on intraocular pressure measurements using the ocular response analyzer. J Glaucoma. 2006;15(5):364–370. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
