LncRNA AWPPH participates in the development of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head by upregulating Runx2
- PMID: 31853285
- PMCID: PMC6909627
- DOI: 10.3892/etm.2019.8185
LncRNA AWPPH participates in the development of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head by upregulating Runx2
Abstract
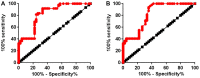
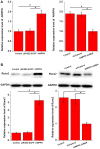
AWPPH is a newly discovered long noncoding (lnc)RNA that plays an oncogenic role in development of several types of malignancies, whiles its involvement in non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head (ONFH) is unknown. Therefore, the present study aimed to investigate the functionality of AWPPH in non-traumatic ONFH. Blood and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) were obtained from both non-traumatic ONFH patients and healthy controls, and expression of AWPPH in those tissues was detected by RT-qPCR. Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis was performed to investigate the diagnostic value of lncRNA AWPPH expression for non-traumatic ONFH. Bone morphogenic protein (BMP-2) was used to treat MSCs to induce osteogenic differentiation and the effects on lncRNA AWPPH expression was detected by RT-qPCR. LncRNA AWPPH overexpression and short hairpin (sh)RNA silencing cell lines were established and the effects on runt-related transcription factor 2 (Runx2) expression were detected by western blotting. It was demonstrated that AWPPH was significantly downregulated in non-traumatic ONFH patients compared with in healthy controls in both MSCs and serum. Expression of AWPPH in MSCs and serum is a sensitive diagnostic marker for non-traumatic ONFH. Expression of AWPPH exhibited no significant correlation with patients' age, gender and living habits, but was significantly correlated with course of disease. BMP-2 treatment significantly increased the expression level of AWPPH in human MSCs from bone marrow (hMSC-BM). AWPPH overexpression promoted, while AWPPH short hairpin RNA silencing inhibited the expression of Runx2 expression in hMSC-BM cells. Therefore, it was concluded that lncRNA AWPPH may participate in the development of ONFH by upregulating Runx2.
Keywords: Runx2; long noncoding RNA AWPPH; mesenchymal stem cells; non-traumatic osteonecrosis of femoral head.
Copyright: © Chen et al.
Figures


References
-
- Okazaki S, Nagoya S, Matsumoto H, Mizuo K, Sasaki M, Watanabe S, Yamashita T, Inoue H. Development of non-traumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head requires toll-like receptor 7 and 9 stimulations and is boosted by repression on nuclear factor kappa B in rats. Lab Invest. 2015;95:92–99. doi: 10.1038/labinvest.2014.134. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
