Glioblastoma Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Enhance Stemness and Tumorigenicity of Glioma Cells by Transferring Notch1 Protein
- PMID: 31853695
- PMCID: PMC11448788
- DOI: 10.1007/s10571-019-00771-8
Glioblastoma Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Enhance Stemness and Tumorigenicity of Glioma Cells by Transferring Notch1 Protein
Abstract
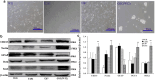
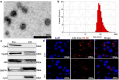
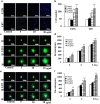
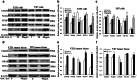
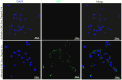
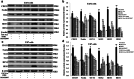
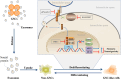
Exosomes contain plenty of bioactive information, playing an important role in intercellular communication by transfer their bioactive molecular contents to recipient cells. Glioblastoma stem cells (GSCs) and non-GSC glioma cells coexist in GBM microenvironment; GSC-released exosomes contain intracellular signaling molecules, which may affect the biological phenotypes of recipient cells. However, whether GSC exosomes could affect the biological phenotype of non-GSC glioma cells has not yet been defined. To explore whether GSC exosomes could reprogramme non-GSC glioma cells into GSCs and its possible mechanism involved, non-GSC glioma cells were treated with GSCs released exosomes; the potential mechanisms of action were studied with RNA interference, Notch inhibitors and Western blot analysis. The proliferation, neurosphere formation, invasive capacities, and tumorigenicity of non-GSC glioma cells were increased significantly after GSC exosome treatment; Notch1 signaling pathway was activated in GSCs; Notch1 protein was highly enriched in GSC exosomes; Notch1 signaling pathway and stemness-related protein expressions were increased in GSC exosome treated non-GSC glioma cells and these cell generated tumor tissues; Notch1 protein expression in GSCs and their exosomes, and the neurosphere formation of GSCs were decreased by Notch1 RNA interference; Notch1 signaling pathway protein and stemness protein expressions were decreased in GSC exosome treated non-GSC glioma cells by Notch1 RNA interference and Notch inhibitors. The findings in this study indicated that GSC exosomes act as information carriers, mediated non-GSC glioma cell dedifferentiation into GSCs by delivering Notch1 protein through Notch1 signaling activation, and enhanced stemness and tumorigenicity of non-GSC glioma cells.
Keywords: Dedifferentiation; Exosomes; Glioblastoma stem cells; Glioma cells; Notch1.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures







References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

