Intraindividual Comparison between Gadoxetate-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Dynamic Computed Tomography for Characterizing Focal Hepatic Lesions: A Multicenter, Multireader Study
- PMID: 31854149
- PMCID: PMC6923212
- DOI: 10.3348/kjr.2019.0363
Intraindividual Comparison between Gadoxetate-Enhanced Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Dynamic Computed Tomography for Characterizing Focal Hepatic Lesions: A Multicenter, Multireader Study
Abstract
Objective: To compare the diagnostic accuracy of dynamic computed tomography (CT) and gadoxetate-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) for characterization of hepatic lesions by using the Liver Imaging Reporting and Data System (LI-RADS) in a multicenter, off-site evaluation.
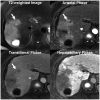
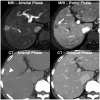
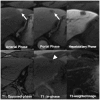
Materials and methods: In this retrospective multicenter study, we evaluated 231 hepatic lesions (114 hepatocellular carcinomas [HCCs], 58 non-HCC malignancies, and 59 benign lesions) confirmed histologically in 217 patients with chronic liver disease who underwent both gadoxetate-enhanced MRI and dynamic CT at one of five tertiary hospitals. Four radiologists at different institutes independently reviewed all MR images first and the CT images 4 weeks later. They evaluated the major and ancillary imaging features and categorized each hepatic lesion according to the LI-RADS v2014. Diagnostic performance was calculated and compared using generalized estimating equations.
Results: MRI showed higher sensitivity and accuracy than CT for diagnosing hepatic malignancies; the pooled sensitivities, specificities, and accuracies for categorizing LR-5/5V/M were 59.0% vs. 72.4% (CT vs. MRI; p < 0.001), 83.5% vs. 83.9% (p = 0.906), and 65.3% vs. 75.3% (p < 0.001), respectively. CT and MRI showed comparable capabilities for differentiating between HCC and other malignancies, with pooled accuracies of 79.9% and 82.4% for categorizing LR-M, respectively (p = 0.139).
Conclusion: Gadoxetate-enhanced MRI showed superior accuracy for categorizing LR-5/5V/M in hepatic malignancies in comparison with dynamic CT. Both modalities had comparable accuracies for distinguishing other malignancies from HCC.
Keywords: Computed tomography; Contrast media; Data systems; Gadolinium ethoxybenzyl DTPA; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Magnetic resonance imaging.
Copyright © 2019 The Korean Society of Radiology.
Conflict of interest statement
The funder Bayer Korea Ltd. had no role in the study design; the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data; the writing of the report; or the decision to submit the manuscript for publication.
Figures


References
-
- Marrero JA, Kulik LM, Sirlin CB, Zhu AX, Finn RS, Abecassis MM, et al. Diagnosis, staging, and management of hepatocellular carcinoma: 2018 practice guidance by the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases. Hepatology. 2018;68:723–750. - PubMed
-
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2018;69:182–236. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
