A hybrid and scalable error correction algorithm for indel and substitution errors of long reads
- PMID: 31856721
- PMCID: PMC6923905
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-019-6286-9
A hybrid and scalable error correction algorithm for indel and substitution errors of long reads
Abstract
Background: Long-read sequencing has shown the promises to overcome the short length limitations of second-generation sequencing by providing more complete assembly. However, the computation of the long sequencing reads is challenged by their higher error rates (e.g., 13% vs. 1%) and higher cost ($0.3 vs. $0.03 per Mbp) compared to the short reads.
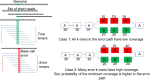
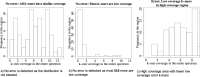
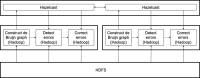
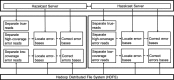
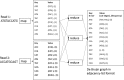
Methods: In this paper, we present a new hybrid error correction tool, called ParLECH (Parallel Long-read Error Correction using Hybrid methodology). The error correction algorithm of ParLECH is distributed in nature and efficiently utilizes the k-mer coverage information of high throughput Illumina short-read sequences to rectify the PacBio long-read sequences.ParLECH first constructs a de Bruijn graph from the short reads, and then replaces the indel error regions of the long reads with their corresponding widest path (or maximum min-coverage path) in the short read-based de Bruijn graph. ParLECH then utilizes the k-mer coverage information of the short reads to divide each long read into a sequence of low and high coverage regions, followed by a majority voting to rectify each substituted error base.
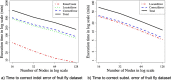
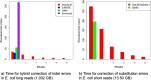
Results: ParLECH outperforms latest state-of-the-art hybrid error correction methods on real PacBio datasets. Our experimental evaluation results demonstrate that ParLECH can correct large-scale real-world datasets in an accurate and scalable manner. ParLECH can correct the indel errors of human genome PacBio long reads (312 GB) with Illumina short reads (452 GB) in less than 29 h using 128 compute nodes. ParLECH can align more than 92% bases of an E. coli PacBio dataset with the reference genome, proving its accuracy.
Conclusion: ParLECH can scale to over terabytes of sequencing data using hundreds of computing nodes. The proposed hybrid error correction methodology is novel and rectifies both indel and substitution errors present in the original long reads or newly introduced by the short reads.
Keywords: Hadoop; Hybrid error correction; Illumina; NoSQL; PacBio.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genome sequence assembly algorithms and misassembly identification methods.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Nov;49(11):11133-11148. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07919-8. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36151399 Review.
-
ARAMIS: From systematic errors of NGS long reads to accurate assemblies.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Nov 5;22(6):bbab170. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab170. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 34013348 Free PMC article.
-
QuorUM: An Error Corrector for Illumina Reads.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 17;10(6):e0130821. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0130821. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26083032 Free PMC article.
-
Accurate self-correction of errors in long reads using de Bruijn graphs.Bioinformatics. 2017 Mar 15;33(6):799-806. doi: 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw321. Bioinformatics. 2017. PMID: 27273673 Free PMC article.
-
A comprehensive evaluation of long read error correction methods.BMC Genomics. 2020 Dec 21;21(Suppl 6):889. doi: 10.1186/s12864-020-07227-0. BMC Genomics. 2020. PMID: 33349243 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genome sequence assembly algorithms and misassembly identification methods.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Nov;49(11):11133-11148. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07919-8. Epub 2022 Sep 23. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 36151399 Review.
-
A review of the pangenome: how it affects our understanding of genomic variation, selection and breeding in domestic animals?J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2023 May 5;14(1):73. doi: 10.1186/s40104-023-00860-1. J Anim Sci Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37143156 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequencing DNA with nanopores: Troubles and biases.PLoS One. 2021 Oct 1;16(10):e0257521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0257521. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34597327 Free PMC article.
-
NmTHC: a hybrid error correction method based on a generative neural machine translation model with transfer learning.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jun 7;25(1):573. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10446-4. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38849740 Free PMC article.
-
Next-generation fungal identification using target enrichment and Nanopore sequencing.BMC Genomics. 2023 Oct 2;24(1):581. doi: 10.1186/s12864-023-09691-w. BMC Genomics. 2023. PMID: 37784013 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Das AK, Lee K, Park S-J. Parlech: Parallel long-read error correction with hadoop. In: 2018 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine (BIBM). IEEE: 2018. p. 341–8. 10.1109/bibm.2018.8621549.
-
- Lou D. I., Hussmann J. A., McBee R. M., Acevedo A., Andino R., Press W. H., Sawyer S. L. High-throughput DNA sequencing errors are reduced by orders of magnitude using circle sequencing. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2013;110(49):19872–19877. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1319590110. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

