Modified regional citrate anticoagulation is optimal for hemodialysis in patients at high risk of bleeding: a prospective randomized study of three anticoagulation strategies
- PMID: 31856749
- PMCID: PMC6924029
- DOI: 10.1186/s12882-019-1661-y
Modified regional citrate anticoagulation is optimal for hemodialysis in patients at high risk of bleeding: a prospective randomized study of three anticoagulation strategies
Abstract
Background: Recommended regular saline flushing presents clinical ineffectiveness for hemodialysis (HD) patients at high risk of bleeding with heparin contraindication. Regional citrate anticoagulation (RCA) has previously been used with a Ca2+ containing dialysate with prefiltered citrate in one arm (RCA-one). However, anticoagulation is not always achievable and up to 40% results in serious clotting in the venous expansion chamber. In this study, we have transferred one-quarter of the TSC from the prefiltered to the post filter based on RCA-one, which we have called RCA-two. The objective of this study was to compare the efficacy and safety of RCA-two with either saline flushing or RCA-one in HD patients with a high bleeding risk.
Method: In this investigator-initiated, multicenter, controlled, prospective, randomized clinical trial, 52 HD patients (77 sessions) were randomized to the RCA-2 and RCA-one group in part one of the trial, and 45 patients (64 sessions) were randomized to the RCA-2 and saline group in part two of the trial. Serious clotting events, adverse events and blood analyses were recorded.
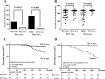
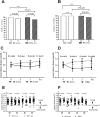
Results: Serious clotting events in the RCA-two group were significantly lower compared with the RCA-one and saline group (7.89% vs. 30.77%, P = 0.011; 3.03% vs. 54.84%, P < 0.001, respectively). The median circuit survival time was 240 min (IQR 240 to 240) in the RCA-two group, was significantly longer than 230 min (IQR 155 to 240, P < 0.001) in the RCA-one group and 210 min (IQR 135 to 240, P = 0.003) in the saline group. The majority of the AEs were hypotension, hypoglycemia and chest tightness, most of which were mild in intensity. Eight patients (20.51%) in the RCA-one group, 4 patients (12.90%) in the saline group and 10 patients (26.31%) in the RCA-two group, P > 0.05.
Conclusions: Our data demonstrated that the modified anticoagulation protocol was more effective and feasible during hemodialysis therapy for patients at high risk of bleeding.
Trial registration: GDREC, GDREC2017250H. Registered February 2, 2018; retrospectively registered.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Khwaja A. KDIGO Clinical practice guidelines for acute kidney disease. Kidney Int. 2012;120:c179–c184. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

